A simple, safe and effective approach to prevent postdural puncture headache: epidural saline injection
- PMID: 25610098
- PMCID: PMC4261270
A simple, safe and effective approach to prevent postdural puncture headache: epidural saline injection
Abstract
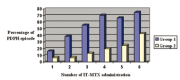
Objective: In this study, we investigated the safety and effectiveness of epidural saline injection to prevent post-dural puncture headache (PDPH) in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Materials and methods: Thirty-three patients with ALL undergoing induction therapy were accepted for the study. Four to six courses of intrathecal methotrexate therapy were administered to each patient for central nervous system prophylaxis. Patients were divided into two groups. Lumbar puncture (LP) was performed without any additional intervention in the first group (18 cases), whereas 20 mL of isotonic saline was injected into the epidural space in the second group (15 cases). The frequency and severity of PDPH were compared between the two groups.
Results: Thirteen patients from the first group and five patients from the second group experienced at least one PDPH episode. In total, 54 PDPH episodes were reported in both groups. The rate of headache due to the LP was significantly higher in the first group than in the second group (48.8% vs. 16.4%, p<0.001). On the other hand, the severity of pain was also significantly higher in the first group (mean pain scores were 5.6 ± 1.62 vs. 3.07 ± 1.18, p<0.001). Furthermore, two patients from the first group (11.11%) developed generalized convulsion attacks, and one of those patients experienced pulmonary arrest necessitating respiratory support. No serious complications were observed in the second group.
Conclusions: Our study shows that isotonic saline injection into the epidural space after LP is a safe and effective approach to prevent PDPH and related complications.
Amaç: Bu çalışmada Akut Lenfoblastik Lösemili (ALL) olgularda epidural salin enjeksiyonunun (ESE) Dural Ponksiyon Sonrası Başağrısı (DPSB)’ nı önlemede etkinliğini ve güvenilirliğini araştırdık.
Gereç ve yöntem: Remisyon indüksiyon tedavisi uygulanmış 33 ALL hastası çalışmaya kabul edildi. Merkezi Sinir Sistemi (MSS) profilaksisi amacıyla her bir hastaya 4 ile 6 kür İntratekal Metotreksat (İT-MTX) tedavisi uygulandı.. Hastalar iki gruba ayrıldı. Birinci grupta (18 olgu) herhangi bir ek uygulama yapılmaksızın Lomber Ponksiyon (LP) yapılırken, ikinci grupta (15 olgu) epidural mesafeye 20 ml izotonik salin enjekte edildi. İki grup arasında DPSB sıklığı ve şiddeti karşılaştırıldı.
Bulgular: Birinci gruptan 13 hasta ve ikinci gruptan 5 hasta en az bir DPSB epizodu yaşadı. Her iki grupta toplam olarak 54 DPSB epizodu gözlendi. Lomber Ponksiyona bağlı başağrısı oranı birinci grupta ikinci gruptan anlamlı olarak daha yüksekti (% 48,80 e karşı % 16,4, p<0,001). Öte yandan birinci grupta ağrının şiddeti de anlamlı olarak daha fazlaydı (ortalama ağrı skorları 5,6 ± 1,62 ye karşı 3,07 ± 1,18, p<0,001). Ek olarak ilk gruptaki iki hastada (%11,11) jeneralize konvülzyon atağı gelişmesine ve bunlardan birinin solunum desteği gerektiren pulmoner arrest ile komplike olmasına rağmen ikinci grupta herhangi bir ciddi komplikasyon gözlenmedi.
Sonuç: Bizim çalışmamız, Lomber Ponksiyon sonrası epidural mesafeye izotonik salin enjeksiyonunun DPSB ve ilişkili komplikasyonların önlenmesinde etkin ve güvenli bir yaklaşım olduğunu gösterdi.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Central nervous system prophylaxis; Epidural saline injection; Post-dural puncture headache.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is epidural dexamethasone effective in preventing postdural puncture headache?Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2014 Sep;52(3):95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.aat.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2014. PMID: 25199696 Clinical Trial.
-
Continuous epidural pumping of saline contributes to prevent and treat postdural puncture headache.J Clin Anesth. 2016 Nov;34:154-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.03.066. Epub 2016 May 5. J Clin Anesth. 2016. PMID: 27687364
-
The Relationship of Body Mass Index with the Incidence of Postdural Puncture Headache in Parturients.Anesth Analg. 2015 Aug;121(2):451-6. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000802. Anesth Analg. 2015. PMID: 25993388
-
Efficacy and Safety of Prophylactic Intrathecal or Epidural Normal Saline for Preventing Post-Dural Puncture Headache After Dural Puncture: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.J Pain Res. 2025 Feb 26;18:915-927. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S494237. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 40027214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rational approach to the cause, prevention and treatment of postdural puncture headache.CMAJ. 1993 Oct 15;149(8):1087-93. CMAJ. 1993. PMID: 8221447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Obesity on Lumbar Puncture Outcomes in Adults with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Lymphoma: Experience at an Academic Reference Center.Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2019 Jul 1;13(3):146-152. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31649805 Free PMC article.
-
Post-dural puncture headache: a prospective study on incidence, risk factors, and clinical characterization of 285 consecutive procedures.BMC Neurol. 2022 Jul 14;22(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02785-0. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35836140 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the optimal duration of bed rest in the supine position to reduce complications after lumbar puncture combined with intrathecal chemotherapy: a multicenter prospective randomized controlled trial.Support Care Cancer. 2018 Sep;26(9):2995-3002. doi: 10.1007/s00520-018-4142-0. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Support Care Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29546527 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lumbar Puncture Complications: A Review of Current Literature.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024 Aug;28(8):803-813. doi: 10.1007/s11916-024-01262-2. Epub 2024 May 22. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024. PMID: 38776003 Review.
-
Trans-nasal sphenopalatine ganglion block for post-dural puncture headache management: a meta-analysis of randomized trials.Braz J Anesthesiol. 2023 Nov-Dec;73(6):782-793. doi: 10.1016/j.bjane.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37422191 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Itakura H, Coutre SE. acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults. In: Greer JP, Foerster J, Rodgers GM, Paraskevas F, Glader B, Arber DA, Means RT Jr, editors. Wintrobe’s Clinical Hematology. 12th Edition. Wolters Kluwer / Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2009. pp. 1820–42.
-
- Armitage JO, Longo DL. Malignancies of Lymphoid Cells. In: Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, editors. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 16th Edition. McGRAW – HILL Co; New York: 2005. pp. 641–55.
-
- Gaiser R. Postdural puncture headache. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2006;19:249–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources