Determination of linear x-ray attenuation coefficients of pathological brain tissues and use of filters in tissue contrast enhancement in computed tomography
- PMID: 25610123
- PMCID: PMC4261332
- DOI: 10.5152/eajm.2010.17
Determination of linear x-ray attenuation coefficients of pathological brain tissues and use of filters in tissue contrast enhancement in computed tomography
Abstract
Objective: X-ray attenuation coefficients are used in common radiological, pathological and spectroscopic examinations and in the determination of the radiation dose distribution in biological tissues. In radiology, these coefficients enable diagnosis by differentiating the abnormal tissues from the normal ones using their morphological structure and contrast differences. In this study, our aim is to precisely determine the linear x-ray attenuation coefficients of pathological brain tissues and to use x-ray beam filters to enhance the tissue contrast in computed tomography.
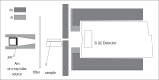
Materials and methods: To directly measure the relative linear attenuation coefficients, an energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy system (EDXRS-Canberra, Si(Li) with DSA-1000 spectrum analyzer 1998; CT, USA) was used with collimators and a medical-purpose x-ray tube (Siemens, Siremobil, 1985; Erlangen, Germany) in a linear geometry.
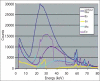
Results: Using a Mo filter with Computed Tomography CT and photon energies from 15 to 25 keV, EDXRS acquisitions were found to significantly distinguish grades of brain tumors (p<0.05). For the data acquired from CT systems with the decreasing filtered photon mean energy, the x-ray attenuation coefficients (i.e., the Hounsfield units) show that the ratio of EDXRS to CT for water's attenuation coefficient are increased. With our suggested x-ray filters, the tissue contrast has been found to be increased in ex vivo brain tumor slices compared with slices scanned in conventional CT scanners.
Conclusion: X-ray attenuations measured with the EDXRS are found to be statistically more reliable because of the length of acquisition times in this study.
Amaç: Temel değişkenler olarak x-ışını azaltma katsayıları radyolojik, patolojik ve spektroskopik incelemelerde ve biyolojik dokularda radyasyon doz dağılımının belirlenmesinde yaygın olarak kullanılmaktadır. Özellikle radyolojide anormal dokuların normal olanlarından biçimsel yapı ve kontrast artışından faydalanarak tanılanmasını sağlar. Bu çalışmada patolojik beyin tümörlerinin lineer x-ışını azaltma katsayılarını hassas bir şekilde tespit etmeye ve bilgisayarlı tomografide (BT) doku kontrastını x-ışını demet filtreleriyle artırmaya çalıştık.
Gereç ve yöntem: Bu çalışmada numunelerin bağıl lineer x-ışını azaltma katsayısının doğrudan ölçümünde enerji ayrımlı bir x-ışını spektroskopi sistemi (EDXRS-Canberra, Si(Li) dedektörü DSA-1000 spektrum analizörüyle, 1998, CT, USA) ile lineer geometride kolimatörler ve bir tıbbi x-ışını tüpü (Siemens, Siremobil, 1985, Erlangen, Almanya) kullanılmıştır. Ayrıca bilgisayarlı tomografi sistemi (Toshiba, XVision/GX, 1994, Nasu, Japonya) Hounsfield birimi (HU) ölçümleri için kullanılmıştır. Önerilen x-ışını demet filtreleri için yapılan ölçümler patolojik olarak tanılanmış çeşitli numunelerde tekrarlanmış ve istatistiki metotlarla değerlendirilmiştir.
Bulgular: BT ölçümlerinde Mo filtre kullanılarak, EDXRS ölçümlerinde 15–25 keV aralığındaki enerjiye sahip fotonlarla beyin tümörlerinin greydleri arasındaki farklılığın daha iyi ayırt edildiği tespit edilmiştir. BT sistemlerinden alınan verilerde filtrelemeyle ortalama foton enerjisinin azaltılması sonucunda x-ışını azaltma katsayıları ya da bu katsayıların suyun azaltma katsayısına oranını gösteren HU artmıştır. Önerdiğimiz x-ışını demet filtreleriyle elde edilen çıkarılmış beyin tümörü kesitlerindeki doku kontrastının konvansiyonel BT tarayıcılarından alınan kesitlere nispeten artmış olduğu bulunmuştur.
Sonuç: EDXRS ile elde edilen lineer x-ışını azaltma katsayıları veri alma sürelerinin uzun olması sebebiyle istatistiki olarak daha güvenilir bulunmuştur.
Keywords: Computed tomography; X-ray attenuation coefficient; X-ray spectral filters; X-ray tube.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Converting computed tomography images into photon interaction coefficients by using stoichiometric calibration and parametric fit models.Med Phys. 2017 Feb;44(2):510-521. doi: 10.1002/mp.12055. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28133756
-
Simulation study of a quasi-monochromatic beam for x-ray computed mammotomography.Med Phys. 2004 Apr;31(4):800-13. doi: 10.1118/1.1668371. Med Phys. 2004. PMID: 15124997
-
A method for estimating radiation interaction coefficients for tissues from single energy CT.Phys Med Biol. 2014 Dec 7;59(23):7479-99. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/23/7479. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Phys Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25393760
-
[Incident Photon Number and Reconstructed Linear Attenuation Coefficients in Iterative CT Image Reconstruction].Igaku Butsuri. 2019;38(4):143-158. doi: 10.11323/jjmp.38.4_143. Igaku Butsuri. 2019. PMID: 30828046 Review. Japanese.
-
X-ray-based attenuation correction for positron emission tomography/computed tomography scanners.Semin Nucl Med. 2003 Jul;33(3):166-79. doi: 10.1053/snuc.2003.127307. Semin Nucl Med. 2003. PMID: 12931319 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Algorithm for Intracranial Lesions in the Emergency Department: Effectiveness of the Relative Brain Volume and Hounsfield Unit Value Measured by Perfusion Tomography.Cureus. 2024 Jun 3;16(6):e61591. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61591. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38962639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hendee W R. Physics and applications of medical imaging. Rev Mod Phys. 1999;71:444–50.
-
- Baldelli P, Taibi A, Tuffanelli A, Gambaccini Quasi-monochromatic x-rays for diagnostic radiology. M. Phys Med Biol. 2003;48:3653–65. - PubMed
-
- Gingold EL, Wu X, Barnes GT. Contrast and dose with Mo-Mo, Mo-Rh, and Rh-Rh target-filter combinations in mammography. Radiology. 1995;195:639–44. - PubMed
-
- Verhaegen F, Castellano IA. Microdosimetric characterisation of 28 kVp Mo/Mo, Rh/Rh, Rh/Al, W/Rh and Mo/Rh mammography X ray spectra. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2002;99:393–6. - PubMed
-
- Blake GM, McKeeney DB, Chhaya SC, et al. Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry: the effects of beam hardening on bone density measurements. Med Phys. 1992;19:459–65. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources