Infant botulism
- PMID: 25610131
- PMCID: PMC4261338
- DOI: 10.5152/eajm.2010.25
Infant botulism
Abstract
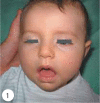
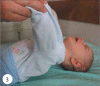
Infant botulism is a rare condition caused by intestinal colonization with Clostridium botulinum. The enteric toxin causes intestinal immobility and progressive descending paralysis due to the effect on acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction and other cholinergic nerve terminals, particularly in the gut. Herein, we report an infant with infantile botulism because of rare clinically entity, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment recover no squeal.
İnfant botilismus Clostridium botulinum ile barsakta kolonizasyon sonucu meydana gelen nadir bir klinik durumdur. Bu enterik toksin barsağa ulaştığında öncelikle intestinal motiliteyi durdurur, daha sonra ise başta barsak olmak üzere nöromuskuler kavşaktaki asetilkolin salınımına neden olarak ilerleyici, aşağıdan başlayan yukarıya doğru ilerleyen paraliziler meydana getirir. Burada çok nadir rastanan bir infantil botilismus vakası sunulmaktadır. Erken tanı ve uygun tedavinin sekelsiz iyileşmede önemi vurgulanmaktadır.
Keywords: Botulism; Clostridium botulinum; Infant pitosis.
Figures
References
-
- Arnon SS, Damus K, Chin J. Infant botulism: epidemiology and relation to sudden infant death syndrome. Epidemiol Rev. 1981;3:45–66. - PubMed
-
- Pickett J, Berg B, Chaplin E, Brunstetter-Shafer MA. Syndrome of botulism in infancy: clinical and electrophysiologic study. N Engl J Med. 1976;295:770–2. - PubMed
-
- Armada M, Love S, Barrett E, Monroe J, Peery D, Sobel J. Foodborne botulism in a six-month-old infant caused by home-canned baby food. Ann Emerg Med. 2003;42:226–9. [Erratum in Ann Emerg Med. 2003; 42:600]. - PubMed
-
- Fox CK, Keet CA, Strober JB. Recent advances in infant botulism. Pediatr Neurol. 2005;32:149–54. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources