Diffuse idiopathic calcinosis cutis in an adult: a rare case
- PMID: 25610312
- PMCID: PMC4261459
- DOI: 10.5152/eajm.2014.29
Diffuse idiopathic calcinosis cutis in an adult: a rare case
Abstract
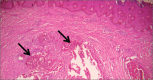
Idiopathic calcinosis cutis is a condition involving the deposition of calcium salts in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The disease is a pathological condition of unknown origin and hence is idiopathic. The salt deposition is confined to areas such as the breast and vulva in females and scrotum and penis in males. Diffuse calcification with multiple complications in an adult is a rare entity. Only one such case has been reported in literature. A 59-year-old female presented to us with swelling of the right elbow, multiple calcific nodular lesions all over her fingers approximately 0.5x0.5 cm in size, and ulcers on her left great toe and right thumb with pain for the past two months. The ulcers were 2x2 cm and were observed to be healing without active discharge or signs of inflammation. The elbow was diffusely swollen and tender. Flexion deformity was present at the elbow. X-ray of hand and feet revealed calcinosis of the elbow and interphalangeal joints of the foot and hand. Blood tests revealed elevated C-reactive protein levels of 24 mg/dL, elevated Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) of 52 mm/hr., serum calcium of 9.7 mg/dL and a serum phosphorous of 5 mg/dL. Cultures from the foot ulcer were positive for methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Workup for collagen vascular disease was negative. Histopathology confirmed calcinosis cutis. Treatment involved a conservative approach, including physiotherapy for the flexion deformity, antibiotics for MRSA, analgesics for pain relief and daily dressings. This case demonstrates that if a patient presents with multiple chalky nodular lesions with or without ulceration, pain and discharge involving areas of the upper limb or lower limb, diagnosis of idiopathic calcinosis cutis could be considered as a differential, despite its common confinement to the scrotum, breast, vulva and penis.
İdiyopatik Calcinosis Cutis, deri ve deri altı dokuda kalsiyum tuzlarının çökelmesini içeren bir durumdur. Hastalık sebebi bilinmeyen ve bu nedenle idiyopatik bir patolojidir. Tuz birikimi, kadınlarda ve erkeklerde skrotum ve penis, meme ve vulva gibi alanlarda sınırlıdır. Bir yetişkinde birden fazla komplikasyon ile diffüz kalsifikasyonun bulunması nadir bir durumdur. Literatürde bu şekilde sadece bir vaka rapor edilmiştir. Sol ayak başparmağında ağrı, sağ dirsek şişmesi ve sağ başparmak üzerinde 0.5x0.5 cm boyutunda ülserler ile iki ay önce bize başvuran 59 yaşındaki kadında, tüm parmaklarının üzerinde kalsifik nodüler lezyonları bulunmaktaydı. Ülserler 2x2 cm idi ve aktif akıntılı veya enflamasyon belirtileri olmadan iyileşme gözlemlendi. Dirsek diffüz olarak şişmiş ve hassastı. Dirsekte fleksiyon deformitesi mevcuttu. El ve ayakların röntgeninde, ayak ve el dirsek ve interfalengeal eklemlerin kalsinozisi saptandı. Kan testleri 24 mg/dL’lik artmış C-reaktif protein seviyeleri, 52 mm/saat’lik yüksek bir ESR, 9,7 mg/dL serum kalsiyum, 5 mg/dL’lik bir serum fosfor ortaya çıkardı. Ayak ülseri kültürlerinde metisilin dirençli Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pozitif bulunmuştur. Kolajen vasküler hastalık için yapılan çalışma negatifti. Histopatoloji kalsinozis kutisi doğruladı. Tedavi fleksiyon deformitesi için fizyoterapi, MRSA için antibiyotik, ağrı kesici ve günlük pansuman için analjezikler de dahil olmak üzere, konservatif yaklaşım içeriyordu. Bu durum bir hastanın ülser, ağrı ve üst uzuv veya alt ekstremitenin alanlarını içeren akıntılı olduğu ya da olmadığı, birden fazla kireçli nodüler lezyon mevcut olması durumunda, idiyopatik calsinosis cutis’in tanısının skrotum, meme, vulva ve penisde de yaygın olmasına rağmen, bir diferansiyel tanı olarak kabul edilebileceğini göstermektedir.
Keywords: Calcinosis cutis; adult; diffuse; idiopathic.
Figures



References
-
- Aksoy HM, Ozdemir R, Karaaslan O, et al. Incidental idiopathic calcinosis cutis in a rhytidectomy patient. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:1145–7. - PubMed
-
- Özçelik B, Serin IS, Basbug M, et al. Idiopathic calcinosis cutis of the vulva in an elderly woman: a case report. J Reprod Med. 2002;47:597–99. - PubMed
-
- Guermazi A, Grigoryan M, Cordoliani F, et al. Unusually diffuse idiopathic calcinosis cutis. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:268–70. - PubMed
-
- Larralde M, Giachetti A, Caceres MR, et al. Calcinosis cutis following trauma. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:227–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
