Blood-brain barrier breakdown in the aging human hippocampus
- PMID: 25611508
- PMCID: PMC4350773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.032
Blood-brain barrier breakdown in the aging human hippocampus
Abstract
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) limits entry of blood-derived products, pathogens, and cells into the brain that is essential for normal neuronal functioning and information processing. Post-mortem tissue analysis indicates BBB damage in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The timing of BBB breakdown remains, however, elusive. Using an advanced dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI protocol with high spatial and temporal resolutions to quantify regional BBB permeability in the living human brain, we show an age-dependent BBB breakdown in the hippocampus, a region critical for learning and memory that is affected early in AD. The BBB breakdown in the hippocampus and its CA1 and dentate gyrus subdivisions worsened with mild cognitive impairment that correlated with injury to BBB-associated pericytes, as shown by the cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Our data suggest that BBB breakdown is an early event in the aging human brain that begins in the hippocampus and may contribute to cognitive impairment.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
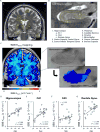
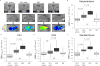


Comment in
-
Dangerous leaks: blood-brain barrier woes in the aging hippocampus.Neuron. 2015 Jan 21;85(2):231-3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.056. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 25611503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apostolova LG, Hwang KS, Andrawis JP, Green AE, Babakchanian S, Morra JH, Cummings JL, Toga AW, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM, et al. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, 3D PIB and CSF biomarker associations with hippocampal atrophy in ADNI subjects. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31:1284–1303. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armulik A, Genové G, Mäe M, Nisancioglu MH, Wallgard E, Niaudet C, He L, Norlin J, Lindblom P, Strittmatter K, et al. Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier. Nature. 2010;468:557–561. - PubMed
-
- Baloyannis SJ, Baloyannis IS. The vascular factor in Alzheimer’s disease: A study in Golgi technique and electron microscopy. J Neurol Sci. 2012;322:117–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG039452/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37AG23084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG039452/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB013456/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- EB000993/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000993/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015922/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG039452/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21EB013456/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R37NS34467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000130/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 7P41EB015922/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG023084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG05142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

