Differential expression of protocadherin-19, protocadherin-17, and cadherin-6 in adult zebrafish brain
- PMID: 25612302
- PMCID: PMC4412781
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.23746
Differential expression of protocadherin-19, protocadherin-17, and cadherin-6 in adult zebrafish brain
Abstract
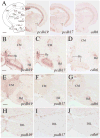
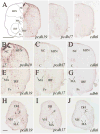
Cell adhesion molecule cadherins play important roles in both development and maintenance of adult structures. Most studies on cadherin expression have been carried out in developing organisms, but information on cadherin distribution in adult vertebrate brains is limited. In this study we used in situ hybridization to examine mRNA expression of three cadherins, protocadherin-19, protocadherin-17, and cadherin-6 in adult zebrafish brain. Each cadherin exhibits a distinct expression pattern in the fish brain, with protocadherin-19 and protocadherin-17 showing much wider and stronger expression than that of cadherin-6. Both protocadherin-19 and protocadherin-17-expressing cells occur throughout the brain, with strong expression in the ventromedial telencephalon, periventricular regions of the thalamus and anterior hypothalamus, stratum periventriculare of the optic tectum, dorsal tegmental nucleus, granular regions of the cerebellar body and valvula, and superficial layers of the facial and vagal lobes. Numerous sensory structures (e.g., auditory, gustatory, lateral line, olfactory, and visual nuclei) and motor nuclei (e.g., oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal motor, abducens, and vagal motor nuclei) contain protocadherin-19 and/or protocadherin-17-expressing cell. Expression of these two protocadherins is similar in the ventromedial telencephalon, thalamus, hypothalamus, facial, and vagal lobes, but substantially different in the dorsolateral telencephalon, intermediate layers of the optic tectum, and cerebellar valvula. In contrast to the two protocadherins, cadherin-6 expression is much weaker and limited in the adult fish brain.
Keywords: RRID: 2DB-GENO-030619-2; RRID: AB_193290; RRID: AB_514497, Roche Cat. no. 11093274910; RRID: BC_129243; RRID: XM_684743; cell adhesion molecules; cerebellum; motor nuclei; sensory systems.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no known conflict of interest to declare from all the authors.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Krüpple-like factors 7 and 6a mRNA expression in adult zebrafish central nervous system.Gene Expr Patterns. 2016 May;21(1):41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Gene Expr Patterns. 2016. PMID: 27364471 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of protocadherin-19 in the nervous system of the embryonic zebrafish.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(5):905-11. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.092882ql. Int J Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19757381
-
Differential expression of cadherins in the developing and adult zebrafish olfactory system.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Oct 18;478(3):269-81. doi: 10.1002/cne.20293. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15368532
-
Protocadherins and diversity of the cadherin superfamily.J Cell Sci. 1996 Nov;109 ( Pt 11):2609-11. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.11.2609. J Cell Sci. 1996. PMID: 8937978 Review.
-
Cadherins and the pathogenesis of epilepsy.Cell Biochem Funct. 2022 Jun;40(4):336-348. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3699. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Cell Biochem Funct. 2022. PMID: 35393670 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping of Morphine-Induced OPRM1 Gene Expression Pattern in the Adult Zebrafish Brain.Front Neuroanat. 2020 Feb 20;14:5. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2020.00005. eCollection 2020. Front Neuroanat. 2020. PMID: 32153369 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association study identifies candidate loci associated to syringomyelia secondary to Chiari-like malformation in Cavalier King Charles Spaniels.BMC Genet. 2018 Mar 22;19(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12863-018-0605-z. BMC Genet. 2018. PMID: 29566674 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptome of anterior regeneration in earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jan;48(1):259-283. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06044-8. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33306150
-
Sexual Dimorphic Distribution of Hypothalamic Tachykinin1 Cells and Their Innervations to GnRH Neurons in the Zebrafish.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 3;11:534343. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.534343. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33763023 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal Growth Abnormalities Underlying Ocular Cranial Nerve Disorders.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2021 Sep 15;7:827-850. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-093019-114307. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34081534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acampora D, Gulisano M, Broccoli V, Simeone A. Otx genes in brain morphogenesis. Prog Neurobiol. 2001;64:69–95. - PubMed
-
- Akins MR, Benson DL, Greer CA. Cadherin expression in the developing mouse olfactory system. J Comp Neurol. 2007;501:483–497. - PubMed
-
- Barthel LK, Raymond PA. Subcellular localization of alpha tubulin an opsin mRNA in the goldfish retina using digoxigenin-labeled cRNA probes detected by alkaline phosphatase and HRP histochemistry. J Neurosci Methods. 1990;48:145–152. - PubMed
-
- Becker T, Redies C. Internal structure of the nucleus rotundus revealed by mapping cadherin expression in the embryonic chicken visual system. J Comp Neurol. 2003;467:536–548. - PubMed
-
- Bishop KM, Goudreau G, O’Leary DD. Regulation of area identity in the mammalian neocortex by Emx2 and Pax6. Science. 2000;288:344–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

