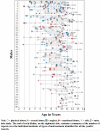
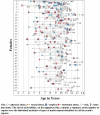
The whole picture: Child maltreatment experiences of youths who were physically abused
- PMID: 25613088
- PMCID: PMC4725308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2014.12.006
The whole picture: Child maltreatment experiences of youths who were physically abused
Abstract
The purpose of the current study was to describe the maltreatment experiences of a sample of urban youths identified as physically abused using the Maltreatment Case Record Abstraction Instrument (MCRAI). The sample (n=303) of 9-12 year old youths was recruited from active child protective services (CPS) cases in 2002-2005, and five years of child protective service records were reviewed. The demographic and maltreatment experiences of MCRAI-identified youths with physical abuse were compared to maltreated youths who were not physically abused and youths who were identified as physically abused by CPS when they entered this longitudinal study. T-tests and chi-square tests were used to compare the demographics and maltreatment experiences of the sample MCRAI-identified physically abused to the sample MCRAI-identified as nonphysically abused maltreated by gender. Of the total sample, 156 (51%) were identified by MCRAI as physically abused and 96.8% of these youth also experienced other types of maltreatment. Whereas youth with the initial CPS identification of physical abuse showed little co-occurrence (37.7%) with other forms of maltreatment. The MCRAI-identified physically abused youths had a significantly higher mean number of CPS reports and higher mean number of incidents of maltreatment than MCRAI-identified nonphysically maltreated youths. Lifeline plots of case record history from the time of first report to CPS to entry into the study found substantial individual variability in maltreatment experiences for both boys and girls. Thus, obtaining maltreatment information from a single report vastly underestimates the prevalence of physical abuse and the co-occurrence of other maltreatment types.
Keywords: Case record abstraction; Child maltreatment; Child protective services; Physical abuse.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emotional abuse in a sample of multiply maltreated, urban young adolescents: issues of definition and identification.Child Abuse Negl. 2009 Jan;33(1):27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2008.12.003. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Child Abuse Negl. 2009. PMID: 19178945 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the sexual abuse experiences of young adolescents.Child Abuse Negl. 2014 Feb;38(2):261-70. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2013.08.021. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Child Abuse Negl. 2014. PMID: 24095179 Free PMC article.
-
Child neglect: definition and identification of youth's experiences in official reports of maltreatment.Child Abuse Negl. 2010 Sep;34(9):647-58. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2010.02.007. Child Abuse Negl. 2010. PMID: 20643482 Free PMC article.
-
Gender Differences in the Maltreatment-Youth Offending Relationship: A Scoping Review.Trauma Violence Abuse. 2023 Apr;24(2):1140-1156. doi: 10.1177/15248380211052106. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2023. PMID: 34907817 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional and behavioral sequelae of childhood maltreatment.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010 Oct;22(5):610-5. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e32833e148a. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010. PMID: 20736837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding child directed caregiver aggression: An examination of characteristics and predictors associated with perpetration.Child Abuse Negl. 2016 Jun;56:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Child Abuse Negl. 2016. PMID: 27131453 Free PMC article.
-
Substantiated childhood maltreatment and young adulthood cannabis use disorders: A pre-birth cohort study.Psychiatry Res. 2017 Oct;256:21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.06.017. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Psychiatry Res. 2017. PMID: 28622571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bae HO, Solomon PL, Gelles RJ. Abuse type and substantiation status varying by recurrence. Children and Youth Services Review. 2007;29:856–869. doi:10.1016/j.childyouth.2007.01.002.
-
- Barnett D, Manly JT, Cicchetti D. Defining child maltreatment: The interface between policy and research. In: Cicchetti D, Toth SL, editors. Child abuse, child development, and social policy. Ablex; Norwood, NJ: 1993. pp. 7–73.
-
- Barth RP, Lloyd EC, Green RL, James S, Leslie LK, Landsverk J. Predictors of placement moves among children with and without emotional and behavioral disorders. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders. 2007;15:46–55. doi:10.1177/10634266070150010501.
-
- Black DA, Heyman RE, Smith Slep AM. Risk factors for child physical abuse. Aggression and Violent Behavior. 2001;6:121–188. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(00)00021-5.
-
- Brown J, Cohen P, Johnson JG, Smailes EM. Childhood abuse and neglect: Specificity of effects on adolescent and young adult depression and suicidality. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 1999;38:1490–1496. doi:10.1097/00004583-199912000-00009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical