Protective effects of polyunsatutared fatty acids supplementation against testicular damage induced by intermittent hypobaric hypoxia in rats
- PMID: 25613908
- PMCID: PMC4307138
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-015-0112-8
Protective effects of polyunsatutared fatty acids supplementation against testicular damage induced by intermittent hypobaric hypoxia in rats
Abstract
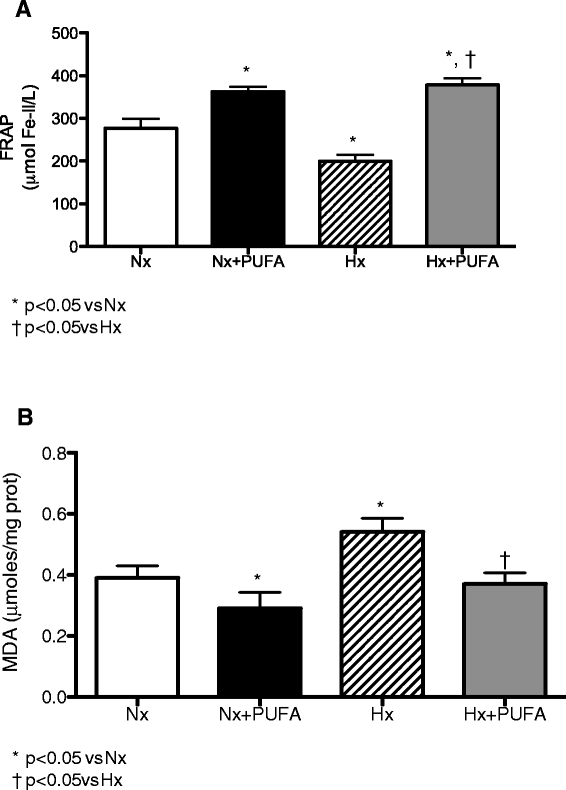
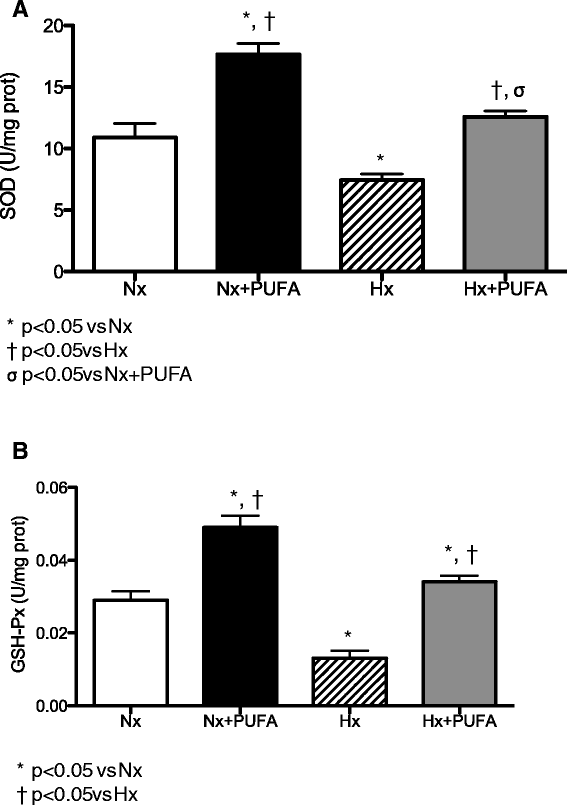
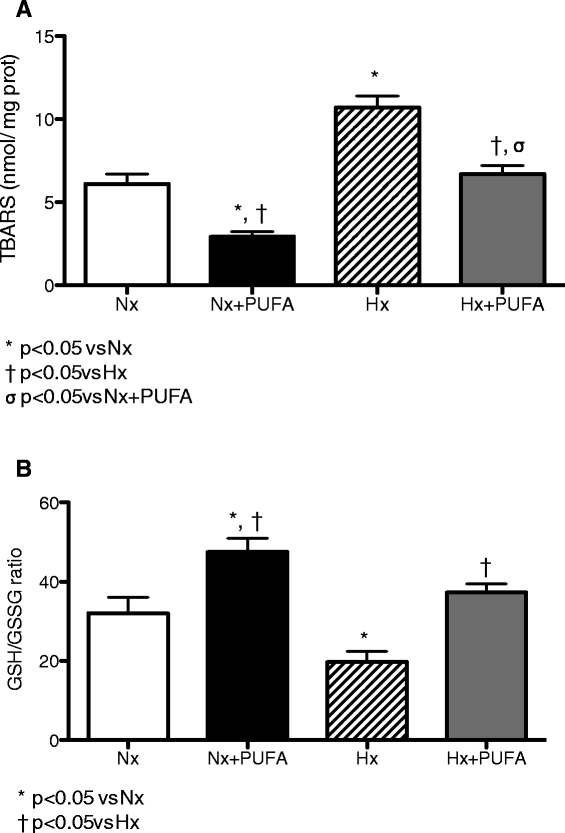
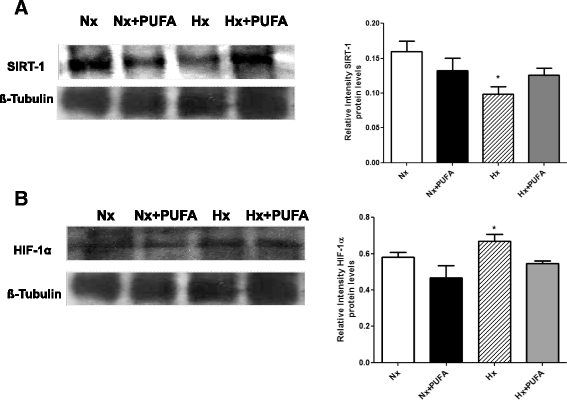
Background: Intermittent hypobaric hypoxia (IHH) induces changes in the redox status and structure in rat testis. These effects may be present in people at high altitudes, such as athletes and miners. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) can be effective in counteracting these oxidative modifications due to their antioxidants properties. The aim of the work was to test whether PUFA supplementation attenuates oxidative damage in testis by reinforcing the antioxidant defense system. The animals were divided into four groups (7 rats per group): normobaric normoxia (~750 tor; pO2 156 mmHg; Nx); Nx + PUFA, supplemented with PUFA (DHA: EPA = 3:1; 0.3 g kg(-1) of body weight per day); hypoxic hypoxia (~428 tor; pO2 90 mmHg; Hx) and, Hx + PUFA. The hypoxic groups were exposed in 4 cycles to 96 h of HH followed by 96 h of normobaric normoxia for 32 days. Total antioxidant capacity (FRAP) and lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde, MDA) in plasma and reduced (GSH)/oxidized glutathione (GSSG) ratio, tissue lipid peroxidation (TBARS) and antioxidant enzymes activity were assessed at the end of the study in testis. Also, SIRTUIN 1 and HIF-1 protein expression in testis were determined.
Results: IHH increased lipid peroxidation in plasma and HIF-1 protein levels in testis. In addition, IHH reduced FRAP levels in plasma, antioxidant enzymes activities and SIRTUIN 1 protein levels in testis. PUFA supplementation attenuated these effects, inducing the increases in FRAP, in the antioxidant enzymes activity and HIF-1 levels.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the IHH model induces a prooxidant status in plasma and testis. The molecular protective effect of PUFA may involve the induction of an antioxidant mechanism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress in rat testis and epididymis under intermittent hypobaric hypoxia: protective role of ascorbate supplementation.J Androl. 2010 May-Jun;31(3):314-21. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.108.007054. Epub 2010 Apr 8. J Androl. 2010. PMID: 20378932
-
Protective effects of quercetin from oxidative/nitrosative stress under intermittent hypobaric hypoxia exposure in the rat's heart.Physiol Int. 2018 Sep 1;105(3):233-246. doi: 10.1556/2060.105.2018.3.23. Physiol Int. 2018. PMID: 30282485
-
Ω3 Supplementation and intermittent hypobaric hypoxia induce cardioprotection enhancing antioxidant mechanisms in adult rats.Mar Drugs. 2015 Feb 4;13(2):838-60. doi: 10.3390/md13020838. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25658050 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between vitamin E requirement and polyunsaturated fatty acid intake in man: a review.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2000 Mar;70(2):31-42. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831.70.2.31. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2000. PMID: 10804454 Review.
-
Hypoxia-induced lipid peroxidation in the brain during postnatal ontogenesis.Physiol Res. 2012;61(Suppl 1):S89-101. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.932374. Physiol Res. 2012. PMID: 22827877 Review.
Cited by
-
The influence of Omega3 fatty acids supplementation against aluminum-induced toxicity in male albino rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Jul;23(14):14354-61. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6578-4. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27055897
-
Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Protection Associated with Intermittent Hypobaric Hypoxia Exposure in a Rat Model: Role of Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 26;19(2):366. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020366. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29373484 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Activity and Lipid Profile of Huitlacoche Mushroom (Ustilago maydis) Produced in Several Maize Genotypes at Different Stages of Development.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2016 Dec;71(4):436-443. doi: 10.1007/s11130-016-0572-3. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27605221
-
Effects of chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia on prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in Chilean miners.Occup Environ Med. 2021 Oct;78(10):753-760. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2020-107232. Epub 2021 May 11. Occup Environ Med. 2021. PMID: 33980699 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of L-carnitine Administration on Sperm and Sex Hormone Levels in a Male Wistar Rat Reproductive System Injury Model in a High-Altitude Hypobaric Hypoxic Environment.Reprod Sci. 2023 Jul;30(7):2231-2247. doi: 10.1007/s43032-022-00948-5. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 36633830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caramelo C, Peña JJ, Castilla A, Justo S, De Solis AJ, Neria F, Peñate S, Gonzalez-Pacheco FR. Response to hypoxia. A systemic mechanism based on the control of gene expression. Medicina. 2006;66:155–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

