High-throughput RNA sequencing reveals the effects of 2,2',4,4' -tetrabromodiphenyl ether on retina and bone development of zebrafish larvae
- PMID: 25614096
- PMCID: PMC4312473
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-014-1194-5
High-throughput RNA sequencing reveals the effects of 2,2',4,4' -tetrabromodiphenyl ether on retina and bone development of zebrafish larvae
Abstract
Background: 2,2',4,4'-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE47) is a prevalent environmental pollutant and has been demonstrated to be a serious toxicant in both humans and animals, but little is known about the molecular mechanism underlying its toxic effect on the early development of vertebrates. BDE47-treated zebrafish larvae were found to present the light-related locomotion reduction in our previous study, therefore, we aimed to use high throughput sequencing to investigate the possible reasons from a transcriptomic perspective.
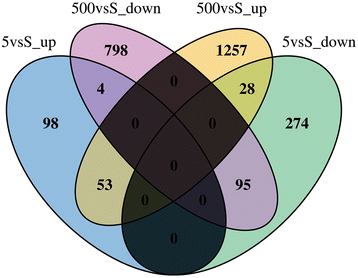
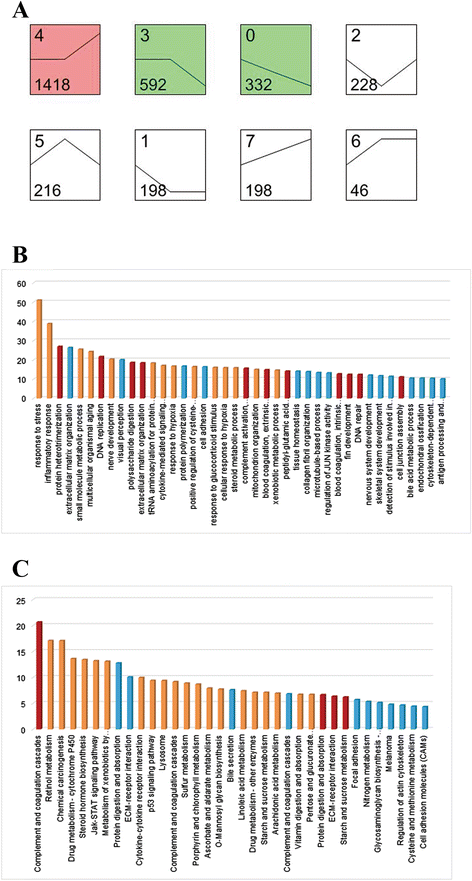
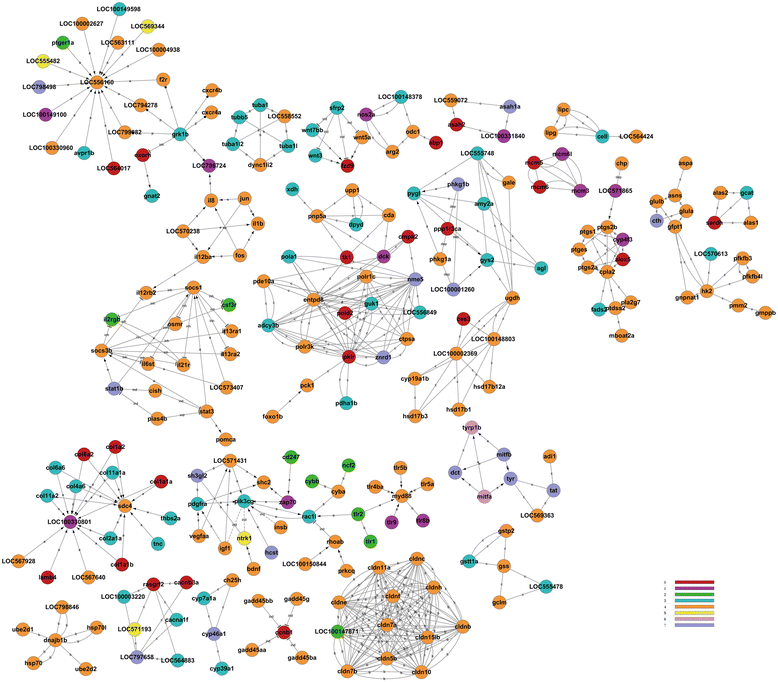
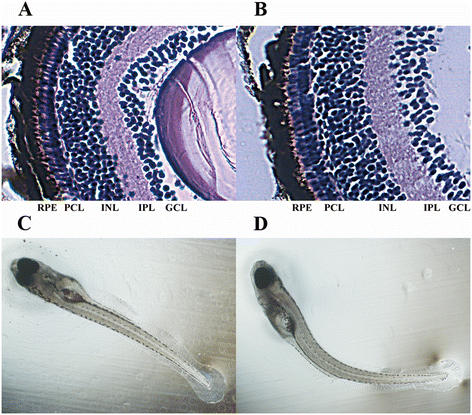
Results: By exposing zebrafish embryos/larvae to 5 μg/l and 500 μg/l BDE47, we measured the influence of BDE47 on the mRNA expression profiles of zebrafish larvae until 6 days post-fertilization, using Illumina HiSeq 2000 sequencing. Differential expression analysis and gene enrichment analysis respectively revealed that a great number of genes, and gene sets based on two popular terminologies, were affected by the treatment of 500 μg/l BDE47. Among them, BDE47 caused changes in the retinal metabolism and related biological processes involving eye morphogenesis and visual perception, as confirmed by disordered photoreceptor arrangement and thickened bipolar cell layer of larval retina from histological observations. Other altered genes such as pth1a and collaborative cathepsin family exhibited disrupted bone development, which was consistent with the body curvature phenotype. The transcriptome of larvae was not significantly affected by the treatment of 5 μg/l BDE47, as well as the treatment of DMSO vehicle.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that high BDE47 concentrations disrupt the eye and bone development of zebrafish larvae based on both transcriptomic and morphological evidences. The abnormal visual perception may result in the alteration of dark adaption, which was probably responsible for the abnormal larval locomotion. Body curvature arose from enhanced bone resorption because of the intensive up-regulation of related genes. We also proposed the larval retina as a novel potential target tissue for BDE47 exposure.
Figures

References
-
- Chernyak SM, Rice CP, Quintal RT, Begnoche LJ, Hickey JP, Vinyard BT. Time trends (1983–1999) for organochlorines and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in rainbow smelt (Osmerus mordax) from Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Superior, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2005;24:1632–1641. doi: 10.1897/04-390R.1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

