Analysis of the age of Panax ginseng based on telomere length and telomerase activity
- PMID: 25614145
- PMCID: PMC5379010
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07985
Analysis of the age of Panax ginseng based on telomere length and telomerase activity
Abstract
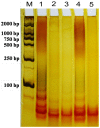
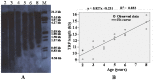
Ginseng, which is the root of Panax ginseng (Araliaceae), has been used in Oriental medicine as a stimulant and dietary supplement for more than 7,000 years. Older ginseng plants are substantially more medically potent, but ginseng age can be simulated using unscrupulous cultivation practices. Telomeres progressively shorten with each cell division until they reach a critical length, at which point cells enter replicative senescence. However, in some cells, telomerase maintains telomere length. In this study, to determine whether telomere length reflects ginseng age and which tissue is best for such an analysis, we examined telomerase activity in the main roots, leaves, stems, secondary roots and seeds of ginseng plants of known age. Telomere length in the main root (approximately 1 cm below the rhizome) was found to be the best indicator of age. Telomeric terminal restriction fragment (TRF) lengths, which are indicators of telomere length, were determined for the main roots of plants of different ages through Southern hybridization analysis. Telomere length was shown to be positively correlated with plant age, and a simple mathematical model was formulated to describe the relationship between telomere length and age for P. ginseng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Effects of arsenic trioxide, ginseng saponin and beta-elemene on telomere-telomerase system in K562 cell line].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Jun;12(3):315-20. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15228657 Chinese.
-
Telomere dynamics in the lower plant Physcomitrella patens.Plant Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;87(6):591-601. doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0299-9. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Plant Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25701469
-
Telomere rapid deletion regulates telomere length in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;27(5):1706-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02059-06. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17189431 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo regulation of telomerase activity and telomere length.Immunol Rev. 2005 Jun;205:104-13. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00267.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15882348 Review.
-
Diet, nutrition and telomere length.J Nutr Biochem. 2011 Oct;22(10):895-901. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.12.001. Epub 2011 Mar 22. J Nutr Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21429730 Review.
Cited by
-
Folic Acid Decreases Astrocyte Apoptosis by Preventing Oxidative Stress-Induced Telomere Attrition.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 20;21(1):62. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010062. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31861819 Free PMC article.
-
Relative Telomere Length and Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) Expression Are Associated with Age in Almond (Prunus dulcis [Mill.] D.A.Webb).Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 20;10(2):189. doi: 10.3390/plants10020189. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498228 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Correlation between Gene Expression and Enzyme Activity of Seven Key Enzymes and Ginsenoside Content in Ginseng in Over Time in Ji'an, China.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 11;18(12):2682. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122682. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29232922 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-mediated regulation of ginsenoside biosynthesis in Panax ginseng and its biotechnological implications.Sci Prog. 2025 Apr-Jun;108(2):368504251332109. doi: 10.1177/00368504251332109. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40165415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of Chromosome Preparation and Karyotype Analysis of Winter Turnip Rape (Brassica rape L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 24;26(15):7127. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157127. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patil D. A. Ethnomedicine to modern medicine: genesis through ages. J. Exp. Sci. 2, 25–29 (2011).
-
- Gillis C. N. Panax ginseng pharmacology: a nitric oxide link? Biochem. Pharmacol. 54, 1–8 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Chen F., Luo J. & Kong L. Determination of 10 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng of different harvest times based on HPLC fingerprints and principal component analysis. Nat. Prod. Res. 27, 851–854 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Kim N. et al. Nontargeted metabolomics approach for age differentiation and structure interpretation of age-dependent key constituents in hairy roots of panax ginseng. J. Nat. Prod. 75, 1777–1784 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Azanza R. V. & Taylor F. J. Are Pyrodinium blooms in the Southeast Asian region recurring and spreading? A view at the end of the millennium. Ambio. 30, 356–364 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

