Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase class II α-isoform PI3K-C2α is required for transforming growth factor β-induced Smad signaling in endothelial cells
- PMID: 25614622
- PMCID: PMC4358250
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601484
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase class II α-isoform PI3K-C2α is required for transforming growth factor β-induced Smad signaling in endothelial cells
Abstract
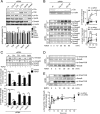
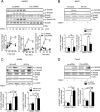
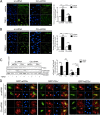
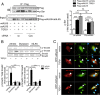
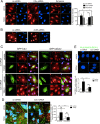
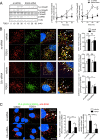
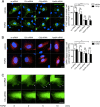
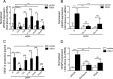
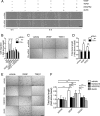
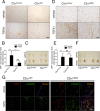
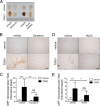
We have recently demonstrated that the PI3K class II-α isoform (PI3K-C2α), which generates phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphates, plays crucial roles in angiogenesis, by analyzing PI3K-C2α knock-out mice. The PI3K-C2α actions are mediated at least in part through its participation in the internalization of VEGF receptor-2 and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1P1 and thereby their signaling on endosomes. TGFβ, which is also an essential angiogenic factor, signals via the serine/threonine kinase receptor complex to induce phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 (Smad2/3). SARA (Smad anchor for receptor activation) protein, which is localized in early endosomes through its FYVE domain, is required for Smad2/3 signaling. In the present study, we showed that PI3K-C2α knockdown nearly completely abolished TGFβ1-induced phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Smad2/3 in vascular endothelial cells (ECs). PI3K-C2α was necessary for TGFβ-induced increase in phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphates in the plasma membrane and TGFβ receptor internalization into the SARA-containing early endosomes, but not for phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate enrichment or localization of SARA in the early endosomes. PI3K-C2α was also required for TGFβ receptor-mediated formation of SARA-Smad2/3 complex. Inhibition of dynamin, which is required for the clathrin-dependent receptor endocytosis, suppressed both TGFβ receptor internalization and Smad2/3 phosphorylation. TGFβ1 stimulated Smad-dependent VEGF-A expression, VEGF receptor-mediated EC migration, and capillary-like tube formation, which were all abolished by either PI3K-C2α knockdown or a dynamin inhibitor. Finally, TGFβ1-induced microvessel formation in Matrigel plugs was greatly attenuated in EC-specific PI3K-C2α-deleted mice. These observations indicate that PI3K-C2α plays the pivotal role in TGFβ receptor endocytosis and thereby Smad2/3 signaling, participating in angiogenic actions of TGFβ.
Keywords: Endosome; Endothelial Cell; PI3K-C2alpha; Phosphatidylinositol Kinase (PI Kinase); Receptor Endocytosis; SARA; SMAD Transcription Factor; TGF-B Receptor; Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-B); Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF).
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Engelman J. A., Luo J., Cantley L. C. (2006) The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 7, 606–619 - PubMed
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B., Guillermet-Guibert J., Graupera M., Bilanges B. (2010) The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 329–341 - PubMed
-
- Virbasius J. V., Guilherme A., Czech M. P. (1996) Mouse p170 is a novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase containing a C2 domain. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 13304–13307 - PubMed
-
- Molz L., Chen Y. W., Hirano M., Williams L. T. (1996) Cpk is a novel class of Drosophila PtdIns 3-kinase containing a C2 domain. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 13892–13899 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

