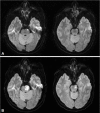
A patient with unilateral periodic leg movements associated with pontine infarction
- PMID: 25614785
- PMCID: PMC4298718
- DOI: 10.14802/jmd.14017
A patient with unilateral periodic leg movements associated with pontine infarction
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez V, Morier J, Hirt L. An episode mimicking a versive seizure in acute bilateral pontine stroke. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18:1141–1142. - PubMed
-
- Kim JS, Lee SB, Park SK, Han SR, Kim YI, Lee KS. Periodic limb movement during sleep developed after pontine lesion. Mov Disord. 2003;18:1403–1405. - PubMed
-
- Bucher SF, Seelos KC, Oertel WH, Reiser M, Trenkwalder C. Cerebral generators involved in the pathogenesis of the restless legs syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1997;41:639–645. - PubMed
-
- Smith RC. Relationship of periodic movements in sleep (nocturnal myoclonus) and the Babinski sign. Sleep. 1985;8:239–243. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources