Severe Leptospira interrogans serovar Icterohaemorrhagiae infection with hepato-renal-pulmonary involvement treated with corticosteroids
- PMID: 25614810
- PMCID: PMC4302624
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.91
Severe Leptospira interrogans serovar Icterohaemorrhagiae infection with hepato-renal-pulmonary involvement treated with corticosteroids
Abstract
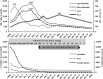
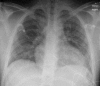
The traditional concept of immediate antibiotic treatment in suspected leptospirosis seems to be especially important for patients up to day 4 of clinical illness. As immune mechanisms probably play a crucial role in advanced leptospirosis with presumed pulmonary hemorrhages, patients might benefit from corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive agents beside antibiotics.
Keywords: Canoeing; Leptospira interrogans; corticosteroids; hepato-pulmonary syndrome; hepato-renal syndrome; leptospirosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of vaccination of cattle with the Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo type hardjoprajitno component of a pentavalent Leptospira bacterin against experimental challenge with Leptospira borgpetersenii serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis.Am J Vet Res. 2012 May;73(5):735-40. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.73.5.735. Am J Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 22533408 Clinical Trial.
-
High virulence in hamsters of four dominant Leptospira serovars isolated from rats in the Philippines.Microbiology (Reading). 2014 Feb;160(Pt 2):418-428. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.072439-0. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Microbiology (Reading). 2014. PMID: 24257815
-
Relation of reproductive disturbance in sheep and Leptospira interrogans serovar Icterohaemorrhagiae infection: Impacts on cellular oxidation status.Microb Pathog. 2019 May;130:65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.02.029. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30831228
-
Leptospira and leptospirosis in China.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2014 Oct;27(5):432-6. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000097. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25061933 Review.
-
Leptospirosis in farmed deer in New Zealand : a review.N Z Vet J. 2007 Jun;55(3):102-8. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2007.36750. N Z Vet J. 2007. PMID: 17534410 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Plasmapheresis and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in the Treatment of Leptospirosis Complicated with Pulmonary Hemorrhages.J Trop Med. 2018 Dec 2;2018:4520185. doi: 10.1155/2018/4520185. eCollection 2018. J Trop Med. 2018. PMID: 30631369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and Genotype Allocation of Pathogenic Leptospira Species in Small Mammals from Various Habitat Types in Germany.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Mar 25;10(3):e0004501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004501. eCollection 2016 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27015596 Free PMC article.
-
Complicated Weil Disease.Balkan Med J. 2016 Jul;33(4):480-1. doi: 10.5152/balkanmedj.2016.16300. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Balkan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27606150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A new model of self-resolving leptospirosis in mice infected with a strain of Leptospira interrogans serovar Autumnalis harboring LPS signaling only through TLR4.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2017 May 24;6(5):e36. doi: 10.1038/emi.2017.16. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2017. PMID: 28536433 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Characterization and Zoonotic Potential of Leptospira interrogans Identified in Small Non-Flying Mammals from Southeastern Atlantic Forest, Brazil.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 27;10(3):62. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed10030062. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40137816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stoddard RA, Gee JE, Wilkins PP, McCaustland K. Hoffmaster AR. Detection of pathogenic Leptospira spp. through TaqMan polymerase chain reaction targeting the LipL32 gene. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009;64:247–255. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation. Human leptospirosis: guidance for diagnosis, surveillance and control. Geneva: World Health Organization & International Leptospirosis Society; 2003.
-
- Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz MM, Lovett MA, et al. Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003;3:757–771. - PubMed
-
- Gsell O. Leptospirosen. In: Gsell O, Mohr W, editors. Infektionskrankheiten. Band II. Krankheiten durch Bakterien. Teil 2. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer; 1968. pp. 826–879.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

