An IL-27/NFIL3 signalling axis drives Tim-3 and IL-10 expression and T-cell dysfunction
- PMID: 25614966
- PMCID: PMC4311884
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7072
An IL-27/NFIL3 signalling axis drives Tim-3 and IL-10 expression and T-cell dysfunction
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: An IL-27/NFIL3 signalling axis drives Tim-3 and IL-10 expression and T-cell dysfunction.Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 8;6:7657. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8657. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26153760 No abstract available.
Abstract
The inhibitory receptor T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 (Tim-3) has emerged as a critical regulator of the T-cell dysfunction that develops in chronic viral infections and cancers. However, little is known regarding the signalling pathways that drive Tim-3 expression. Here, we demonstrate that interleukin (IL)-27 induces nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated (NFIL3), which promotes permissive chromatin remodelling of the Tim-3 locus and induces Tim-3 expression together with the immunosuppressive cytokine IL-10. We further show that the IL-27/NFIL3 signalling axis is crucial for the induction of Tim-3 in vivo. IL-27-conditioned T helper 1 cells exhibit reduced effector function and are poor mediators of intestinal inflammation. This inhibitory effect is NFIL3 dependent. In contrast, tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes from IL-27R(-/-) mice exhibit reduced NFIL3, less Tim-3 expression and failure to develop dysfunctional phenotype, resulting in better tumour growth control. Thus, our data identify an IL-27/NFIL3 signalling axis as a key regulator of effector T-cell responses via induction of Tim-3, IL-10 and T-cell dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
VKK and ACA are paid consultants for Novartis Pharmaceuticals, which has interests in cancer immunotherapy. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


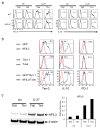

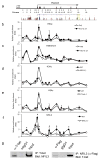
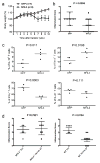

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01NS045937/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045937/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK090105/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS038037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI073748/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R29 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI030048/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS038037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK090105/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AI110649/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

