Horizontal transmission of an R4 clade non-long terminal repeat retrotransposon between the divergent Aedes and Anopheles mosquito genera
- PMID: 25615532
- PMCID: PMC4400214
- DOI: 10.1111/imb.12160
Horizontal transmission of an R4 clade non-long terminal repeat retrotransposon between the divergent Aedes and Anopheles mosquito genera
Abstract
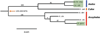
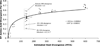
AaegR4_1 and AgamR4_1 are the sole R4 clade non-long terminal repeat (non-LTR) retrotransposons in Aedes aegypti and Anopheles gambiae, two species that diverged approximately 145-200 million years ago. Twelve full-length copies were found in Ae. aegypti and have less than 1% nucleotide (nt) divergence, suggesting recent activity on an evolutionary time scale. Five of these copies have intact open reading frames and the 3.6 kb open reading frame of AaegR4_1.1 has 78% nt identity to AgamR4_1.1. No intact copies were found in An. gambiae. Searches of 25 genomic databases for 22 mosquito species from three genera revealed R4 clade representatives in Aedes and Anopheles genera but not in Culex. Interestingly, these elements are present in all six species of the An. gambiae species complex that were searched but not in 13 other anopheline species. These results combined with divergence vs. age analysis suggest that horizontal transfer is the most likely explanation for the low divergence between R4 clade retrotransposon sequences of the divergent mosquito species from the Aedes and Anopheles genera. This is the first report of the horizontal transfer of an R4 clade non-LTR retrotransposon and the first report of the horizontal transfer of a non-LTR retrotransposon in mosquitoes.
Keywords: evolution; horizontal transfer; mosquito; non-long terminal repeat retrotransposon; transposable elements.
© 2015 The Royal Entomological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Juan non-LTR retrotransposon in mosquitoes: genomic impact, vertical transmission and indications of recent and widespread activity.BMC Evol Biol. 2007 Jul 9;7:112. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-112. BMC Evol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17620143 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and evolutionary analyses of Tango transposons in Aedes aegypti, Anopheles gambiae and other mosquito species.Insect Mol Biol. 2007 Aug;16(4):411-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2007.00735.x. Epub 2007 May 16. Insect Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17506852
-
Non-LTR retrotransposons in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae: unprecedented diversity and evidence of recent activity.Mol Biol Evol. 2003 Nov;20(11):1811-25. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg189. Epub 2003 Jun 27. Mol Biol Evol. 2003. PMID: 12832632
-
Mosquito transposable elements.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Jul;34(7):631-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2004.03.016. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15242704 Review.
-
Jumping the fine LINE between species: horizontal transfer of transposable elements in animals catalyses genome evolution.Bioessays. 2013 Dec;35(12):1071-82. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300072. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 24003001 Review.
Cited by
-
A Survey of Transposon Landscapes in the Putative Ancient Asexual Ostracod Darwinula stevensoni.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 11;12(3):401. doi: 10.3390/genes12030401. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33799706 Free PMC article.
-
Mosquito genomes are frequently invaded by transposable elements through horizontal transfer.PLoS Genet. 2020 Nov 30;16(11):e1008946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008946. eCollection 2020 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 33253164 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptations in energy metabolism and gene family expansions revealed by comparative transcriptomics of three Chagas disease triatomine vectors.BMC Genomics. 2018 Apr 27;19(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4696-8. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29699489 Free PMC article.
-
Hybridogenesis and a potential case of R2 non-LTR retrotransposon horizontal transmission in Bacillus stick insects (Insecta Phasmida).Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 6;7:41946. doi: 10.1038/srep41946. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28165062 Free PMC article.
-
Rare horizontal transmission does not hide long-term inheritance of SINE highly conserved domains in the metazoan evolution.Curr Zool. 2016 Dec;62(6):667-674. doi: 10.1093/cz/zow095. Epub 2016 Sep 11. Curr Zool. 2016. PMID: 29491954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Anisimova M, Gascuel O. Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: A fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst Biol. 2006;55:539–552. - PubMed
-
- Arensburger P, Megy K, Waterhouse RM, Abrudan J, Amedeo P, Antelo B, Bartholomay L, Bidwell S, Caler E, Camara F, Campbell CL, Campbell KS, Casola C, Castro MT, Chandramouliswaran I, Chapman SB, Christley S, Costas J, Eisenstadt E, Feschotte C, Fraser-Liggett C, Guigo R, Haas B, Hammond M, Hansson BS, Hemingway J, Hill SR, Howarth C, Ignell R, Kennedy RC, Kodira CD, Lobo NF, Mao C, Mayhew G, Michel K, Mori A, Liu N, Naveira H, Nene V, Nguyen N, Pearson MD, Pritham EJ, Puiu D, Qi Y, Ranson H, Ribeiro JM, Roberston HM, Severson DW, Shumway M, Stanke M, Strausberg RL, Sun C, Sutton G, Tu ZJ, Tubio JM, Unger MF, Vanlandingham DL, Vilella AJ, White O, White JR, Wondji CS, Wortman J, Zdobnov EM, Birren B, Christensen BM, Collins FH, Cornel A, Dimopoulos G, Hannick LI, Higgs S, Lanzaro GC, Lawson D, Lee NH, Muskavitch MA, Raikhel AS, Atkinson PW. Sequencing of Culex quinquefasciatus establishes a platform for mosquito comparative genomics. Science. 2010;330:86–88. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Besansky NJ, Bedell JA, Benedict MQ, Mukabayire O, Hilfiker D, Collins FH. Cloning and characterization of the white gene from Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol Biol. 1995;4:217–231. - PubMed
-
- BIedler J, Tu Z. Non-LTR retrotransposons in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae: unprecedented diversity and evidence of recent activity. Mol Biol Evol. 2003;20:1811–1825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

