A combined proteomics/genomics approach links hepatitis C virus infection with nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
- PMID: 25616068
- PMCID: PMC4305532
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.028
A combined proteomics/genomics approach links hepatitis C virus infection with nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
Abstract
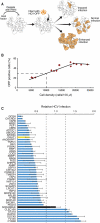
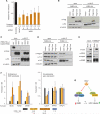
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a leading cause of liver disease, but insight into virus-host interactions remains limited. We systematically used affinity purification/mass spectrometry to define the host interactions of all ten HCV proteins in hepatoma cells. We combined these studies with RNAi knockdown of corresponding genes using a two-step scoring approach to generate a map of 139 high-confidence HCV-host protein-protein interactions. We found mitochondrial proteins highly involved in HCV infection and characterized an interaction between the viral core protein and host protein within bgcn homolog (WIBG). Expression of core prevents WIBG from binding its regular interaction partners Y14 and Magoh, two known mediators of the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway. We discovered that this surveillance pathway is disrupted in HCV-infected cells, causing potentially harmful transcripts to accumulate. Our study provides a comprehensive view of HCV-host interactions and uncovers mechanisms for how HCV perturbs host functions during infection.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


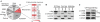

References
-
- Aweya JJ, Tan YJ. Modulation of programmed cell death pathways by the hepatitis C virus. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2011;16:608–618. - PubMed
-
- Balistreri G, Horvath P, Schweingruber C, Zund D, McInerney G, Merits A, Muhlemann O, Azzalin C, Helenius A. The host nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway restricts Mammalian RNA virus replication. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;16:403–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R03 AI069090/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI097552/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM081879/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK060414/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI085056/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM082250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI106754/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R056 AI069090/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI112262/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI091575/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI090935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
