Apolipoprotein A-V deficiency enhances chylomicron production in lymph fistula mice
- PMID: 25617349
- PMCID: PMC4385892
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00339.2014
Apolipoprotein A-V deficiency enhances chylomicron production in lymph fistula mice
Abstract
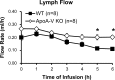
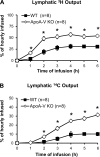
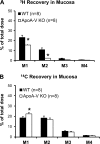
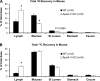
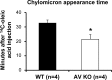
Apolipoprotein A-V (apoA-V), a liver-synthesized apolipoprotein discovered in 2001, strongly modulates fasting plasma triglycerides (TG). Little is reported on the effect of apoA-V on postprandial plasma TG, an independent predictor for atherosclerosis. Overexpressing apoA-V in mice suppresses postprandial TG, but mechanisms focus on increased lipolysis or clearance of remnant particles. Unknown is whether apoA-V suppresses the absorption of dietary lipids by the gut. This study examines how apoA-V deficiency affects the steady-state absorption and lymphatic transport of dietary lipids in chow-fed mice. Using apoA-V knockout (KO, n = 8) and wild-type (WT, n = 8) lymph fistula mice, we analyzed the uptake and lymphatic transport of lipids during a continuous infusion of an emulsion containing [(3)H]triolein and [(14)C]cholesterol. ApoA-V KO mice showed a twofold increase in (3)H (P < 0.001) and a threefold increase in (14)C (P < 0.001) transport into the lymph compared with WT. The increased lymphatic transport was accompanied by a twofold reduction (P < 0.05) in mucosal (3)H, suggesting that apoA-V KO mice more rapidly secreted [(3)H]TG out of the mucosa into the lymph. ApoA-V KO mice also produced chylomicrons more rapidly than WT (P < 0.05), as measured by the transit time of [(14)C]oleic acid from the intestinal lumen to lymph. Interestingly, apoA-V KO mice produced a steadily increasing number of chylomicron particles over time, as measured by lymphatic apoB output. The data suggest that apoA-V suppresses the production of chylomicrons, playing a previously unknown role in lipid metabolism that may contribute to the postprandial hypertriglyceridemia associated with apoA-V deficiency.
Keywords: absorption; intestine.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Aberdeen V, Shepherd PA, Simmonds WJ. Concurrent measurement, in unanaesthetized rats, of intestinal transport and fat absorption from the lumen. Exp Physiol 45: 265–274, 1960. - PubMed
-
- Albers JJ, Kennedy H, Marcovina SM. Evidence that Lp[a] contains one molecule of apo[a] and one molecule of apoB: evaluation of amino acid analysis data. J Lipid Res 37: 192–196, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Beckstead JA, Oda MN, Martin DD, Forte TM, Bielicki JK, Berger T, Luty R, Kay CM, Ryan RO. Structure-function studies of human apolipoprotein A-V: a regulator of plasma lipid homeostasis. Biochemistry 42: 9416–9423, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Beigneux AP, Davies B, Gin P, Weinstein MM, Farber E, Qiao X, Peale F, Bunting S, Walzem RL, Wong JS, Blaner WS, Ding ZM, Melford K, Wongsiriroj N, Shu X, de Sauvage F, Ryan RO, Fong LG, Bensadoun A, Young SG. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 plays a critical role in the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons. Cell Metab 5: 279–291, 2007. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennett S, Simmonds WJ. Absorptive capacity and intestinal motility in unanaesthetized rats during intraduodenal infusion of fat. Exp Physiol 47: 32–38, 1961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

