The widespread role of non-enzymatic reactions in cellular metabolism
- PMID: 25617827
- PMCID: PMC4728180
- DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2014.12.020
The widespread role of non-enzymatic reactions in cellular metabolism
Abstract
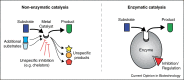
Enzymes shape cellular metabolism, are regulated, fast, and for most cases specific. Enzymes do not however prevent the parallel occurrence of non-enzymatic reactions. Non-enzymatic reactions were important for the evolution of metabolic pathways, but are retained as part of the modern metabolic network. They divide into unspecific chemical reactivity and specific reactions that occur either exclusively non-enzymatically as part of the metabolic network, or in parallel to existing enzyme functions. Non-enzymatic reactions resemble catalytic mechanisms as found in all major enzyme classes and occur spontaneously, small molecule (e.g. metal-) catalyzed or light-induced. The frequent occurrence of non-enzymatic reactions impacts on stability and metabolic network structure, and has thus to be considered in the context of metabolic disease, network modeling, biotechnology and drug design.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Jeong H., Tombor B., Albert R., Oltvai Z.N., Barabási A.L. The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature. 2000;407:651–654. - PubMed
-
- Potter S., Fothergill-Gilmore L.A. Molecular evolution: the origin of glycolysis. Biochem Educ. 1993;21:45–48.
-
- Bräsen C., Esser D., Rauch B., Siebers B. Carbohydrate metabolism in Archaea: current insights into unusual enzymes and pathways and their regulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014;78:89–175. - PMC - PubMed
-
A very comprehensive and informative review, illustrating the variability but also similarities of central carbon metabolism in Archaea.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

