HOS1 regulates Argonaute1 by promoting transcription of the microRNA gene MIR168b in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 25619693
- PMCID: PMC4355216
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.12772
HOS1 regulates Argonaute1 by promoting transcription of the microRNA gene MIR168b in Arabidopsis
Abstract
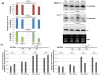
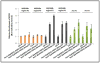
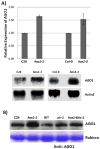
Proper accumulation and function of miRNAs is essential for plant growth and development. While core components of the miRNA biogenesis pathway and miRNA-induced silencing complex have been well characterized, cellular regulators of miRNAs remain to be fully explored. Here we report that High Expression Of Osmotically Responsive Genes1 (HOS1) is a regulator of an important miRNA, mi168a/b, that targets the Argonaute1 (AGO1) gene in Arabidopsis. HOS1 functions as an ubiquitin E3 ligase to regulate plant cold-stress responses, associates with the nuclear pores to regulate mRNA export, and regulates the circadian clock and flowering time by binding to chromatin of the flowering regulator gene Flowering Locus C (FLC). In a genetic screen for enhancers of sic-1, we isolated a loss-of-function Arabidopsis mutant of HOS1 that is defective in miRNA biogenesis. Like other hos1 mutant alleles, the hos1-7 mutant flowered early and was smaller in stature than the wild-type. Dysfunction in HOS1 reduced the abundance of miR168a/b but not of other miRNAs. In hos1 mutants, pri-MIR168b and pre-MIR168b levels were decreased, and RNA polymerase II occupancy was reduced at the promoter of MIR168b but not that of MIR168a. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays revealed that HOS1 protein is enriched at the chromatin of the MIR168b promoter. The reduced miR168a/b level in hos1 mutants results in an increase in the mRNA and protein levels of its target gene, AGO1. Our results reveal that HOS1 regulates miR168a/b and AGO1 levels in Arabidopsis by maintaining proper transcription of MIR168b.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; HIGH EXPRESSION OF OSMOTICALLY RESPONSIVE GENES1; MIR168b; gene expression; microRNA; transcriptional regulation.
© 2015 The Authors The Plant Journal © 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors wish to state that there is no conflict of interest associated with any part of this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Carmell MA, Xuan Z, Zhang M, Hannon GJ. The Argonaute family: tentacles that reach into RNAi, developmental control, stem cell maintenance, and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2002;16:2733–2742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

