Ion transporters in brain tumors
- PMID: 25620102
- PMCID: PMC4363268
- DOI: 10.2174/0929867322666150114151946
Ion transporters in brain tumors
Abstract
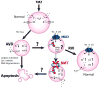
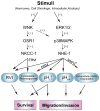
Ion transporters are important in regulation of ionic homeostasis, cell volume, and cellular signal transduction under physiological conditions. They have recently emerged as important players in cancer progression. In this review, we discussed two important ion transporter proteins, sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter isoform 1 (NKCC-1) and sodium-hydrogen exchanger isoform 1 (NHE-1) in Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and other malignant tumors. NKCC-1 is a Na(+)- dependent Cl(-) transporter that mediates the movement of Na(+), K(+), and Cl(-) ions across the plasma membrane and maintains cell volume and intracellular K(+) and Cl(-) homeostasis. NHE-1 is a ubiquitously expressed cell membrane protein which regulates intracellular pH (pH(i)) and extracellular pH (pH(e)) homeostasis and cell volume. Here, we summarized recent pre-clinical experimental studies on NKCC-1 and NHE-1 in GBM and other malignant tumors, such as breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and lung cancer cells. These studies illustrated that pharmacological inhibition or down-regulation of these ion transporter proteins reduces proliferation, increases apoptosis, and suppresses migration and invasion of cancer cells. These new findings reveal the potentials of these ion transporters as new targets for cancer diagnosis and/or treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R, Pavlidis N, Jelic S. ESMO Minimum Clinical Recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of malignant glioma. Ann Oncol. 2005;16(Suppl 1):i64–65. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. - PubMed
-
- Arcangeli A, Crociani O, Lastraioli E, Masi A, Pillozzi S, Becchetti A. Targeting ion channels in cancer: a novel frontier in antineoplastic therapy. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(1):66–93. - PubMed
-
- Fiske JL, Fomin VP, Brown ML, Duncan RL, Sikes RA. Voltage-sensitive ion channels and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25(3):493–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

