Developing genome-wide microsatellite markers of bamboo and their applications on molecular marker assisted taxonomy for accessions in the genus Phyllostachys
- PMID: 25620112
- PMCID: PMC4306134
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08018
Developing genome-wide microsatellite markers of bamboo and their applications on molecular marker assisted taxonomy for accessions in the genus Phyllostachys
Abstract
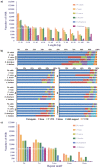
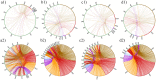
Morphology-based taxonomy via exiguously reproductive organ has severely limitation on bamboo taxonomy, mainly owing to infrequent and unpredictable flowering events of bamboo. Here, we present the first genome-wide analysis and application of microsatellites based on the genome of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) to assist bamboo taxonomy. Of identified 127,593 microsatellite repeat-motifs, the primers of 1,451 microsatellites were designed and 1,098 markers were physically mapped on the genome of moso bamboo. A total of 917 markers were successfully validated in 9 accessions with ~39.8% polymorphic potential. Retrieved from validated microsatellite markers, 23 markers were selected for polymorphic analysis among 78 accessions and 64 alleles were detected with an average of 2.78 alleles per primers. The cluster result indicated the majority of the accessions were consistent with their current taxonomic classification, confirming the suitability and effectiveness of the developed microsatellite markers. The variations of microsatellite marker in different species were confirmed by sequencing and in silico comparative genome mapping were investigated. Lastly, a bamboo microsatellites database (http://www.bamboogdb.org/ssr) was implemented to browse and search large information of bamboo microsatellites. Consequently, our results of microsatellite marker development are valuable for assisting bamboo taxonomy and investigating genomic studies in bamboo and related grass species.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bamboo Transposon Research: Current Status and Perspectives.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2250:257-270. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1134-0_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33900611 Review.
-
Genome skimming-based STMS marker discovery and its validation in temperate hill bamboo Drepanostachyum falcatum.J Genet. 2021;100:28. J Genet. 2021. PMID: 34187975
-
Evaluation of rice and sugarcane SSR markers for phylogenetic and genetic diversity analyses in bamboo.Genome. 2008 Feb;51(2):91-103. doi: 10.1139/g07-101. Genome. 2008. PMID: 18356943
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analyses of the bZIP Transcription Factor Genes in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 5;20(9):2203. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092203. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31060272 Free PMC article.
-
Limitations, progress and prospects of application of biotechnological tools in improvement of bamboo-a plant with extraordinary qualities.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2013 Jan;19(1):21-41. doi: 10.1007/s12298-012-0147-1. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2013. PMID: 24381435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bamboo Transposon Research: Current Status and Perspectives.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2250:257-270. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1134-0_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33900611 Review.
-
Microsatellite Variation in the Most Devastating Beetle Pests (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) of Agricultural and Forest Crops.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 30;23(17):9847. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179847. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077247 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Chloroplast Genome Determination of Ranunculus sceleratus from Republic of Korea (Ranunculaceae) and Comparative Chloroplast Genomes of the Members of the Ranunculus Genus.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 25;14(6):1149. doi: 10.3390/genes14061149. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372329 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analyses of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in 23 mosquito species genomes: Identification, characterization and distribution (Diptera: Culicidae).Insect Sci. 2019 Aug;26(4):607-619. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12577. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Insect Sci. 2019. PMID: 29484820 Free PMC article.
-
De novo transcriptome assembly, development of EST-SSR markers and population genetic analyses for the desert biomass willow, Salix psammophila.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 20;6:39591. doi: 10.1038/srep39591. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27995985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han J. et al. Diversity of culturable bacteria isolated from root domains of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Microb. Ecol. 58, 363–373 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Lai G. A revision of some species of the genus Phyllostachys (Bambusoideae)(III)(in Chinese). Guihaia 22, 390–393 (2002).
-
- Shiobara F., Ishi T., Terachi T. & Tsunewaki K. Mitochondrial genome differentiation in the genus Phyllostachys. JARQ (Japan) 32, 7–14 (1998).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

