Novel mechanism of plasma prekallikrein (PK) activation by vascular smooth muscle cells: evidence of the presence of PK activator
- PMID: 25620170
- PMCID: PMC4337887
Novel mechanism of plasma prekallikrein (PK) activation by vascular smooth muscle cells: evidence of the presence of PK activator
Abstract
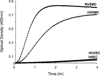
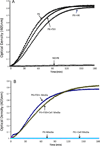
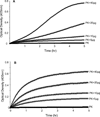
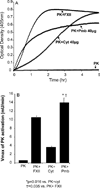
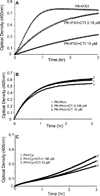
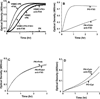
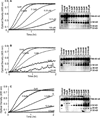
The contribution of plasma prekallikrein (PK) to vascular remodeling is becoming increasingly recognized. Plasma PK is activated when the zymogen PK is digested to an active enzyme by activated factor XII (FXII). Here, we present our findings that vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) activate plasma PK in the absence of FXII. Extracted plasma membrane and cytosolic fractions of VSMCs activate PK, but the rate of PK activation was greater by the membrane fraction. FXII neutralizing antibody did not affect PK activation by extracted proteins of VSMCs. VSMC PKA was inhibited by the serine protease inhibitors such as aprotinin, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, leupeptin and CTI with CI50 of 0.78 μM, 1 mM, 3.13 μM and 40 nM on the cultured cells, respectively. No inhibition of PK activation by cysteine, aspartic acid, and metalloprotease inhibitors was observed. This is the first report of the presence of an intrinsic PKA in VSMC. Considering that VSMCs are normally separated from the circulating blood by endothelial cells, direct PK activation by VSMCs may play a role in disease states like diabetes, hyperlipidemia or hypertension where the endothelial layer is damaged.
Figures




References
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis: An inflammatory disease. NEJM. 1999;340:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Clowes AW, Karnovsky MJ. Suppression by heparin of smooth muscle cell proliferation in injured arteries. Nature. 1977;265:625–626. - PubMed
-
- Jackson CL, Schwartz SM. Pharmacology of smooth muscle cell replication. Hypertension. 1992;20:713–736. - PubMed
-
- Luscher TF, Tanner FC, Tschudi MR, Noll G. Endothelial dysfunction in coronary artery disease. Annu Rev Med. 1993;44:395–418. - PubMed
-
- Shaw Jl, Diamandis EP. Distribution of 15 human kallikreins in tissues and biological fluids. Clin Chem. 2007;53:1423–1432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
