Adolescent pregnancy, birth, and abortion rates across countries: levels and recent trends
- PMID: 25620306
- PMCID: PMC4852976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2014.09.007
Adolescent pregnancy, birth, and abortion rates across countries: levels and recent trends
Abstract
Purpose: To examine pregnancy rates and outcomes (births and abortions) among 15- to 19-year olds and 10- to 14-year olds in all countries for which recent information could be obtained and to examine trends since the mid-1990s.
Methods: Information was obtained from countries' vital statistics reports and the United Nations Statistics Division for most countries in this study. Alternate sources of information were used if needed and available. We present estimates primarily for 2011 and compare them to estimates published for the mid-1990s.
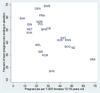
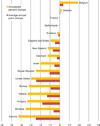
Results: Among the 21 countries with complete statistics, the pregnancy rate among 15- to 19-year olds was the highest in the United States (57 pregnancies per 1,000 females) and the lowest rate was in Switzerland (8). Rates were higher in some former Soviet countries with incomplete statistics; they were the highest in Mexico and Sub-Saharan African countries with available information. Among countries with reliable evidence, the highest rate among 10- to 14-year olds was in Hungary. The proportion of teen pregnancies that ended in abortion ranged from 17% in Slovakia to 69% in Sweden. The proportion of pregnancies that ended in live births tended to be higher in countries with high teen pregnancy rates (p = .02). The pregnancy rate has declined since the mid-1990s in the majority of the 16 countries where trends could be assessed.
Conclusions: Despite recent declines, teen pregnancy rates remain high in many countries. Research on the planning status of these pregnancies and on factors that determine how teens resolve their pregnancies could further inform programs and policies.
Keywords: Cross-national comparisons; Pregnancy outcomes; Pregnancy trends; Teen pregnancies.
Copyright © 2015 Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- UNFPA. Motherhood in childhood: Facing the challenge of adolescent pregnancy: The State of World Population 2013. New York: United Nations Population Fund; 2013. pp. 163–196.
-
- World Health Organization. [Accessed January 27, 2014];Preventing early pregnancy and poor reproductive outcomes among adolescents in developing countries. Available at: http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/adolescence/978924150... - PubMed
-
- National Research Council. Growing up global: The changing transitions to adulthood in developing countries. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2005.
-
- Korenman S, Fales S. The socioeconomic effects of teenage childbearing: A review of the recent literature. New York: Baruch College, City University of New York; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

