SAMP1/YitFc mice develop ileitis via loss of CCL21 and defects in dendritic cell migration
- PMID: 25620669
- PMCID: PMC4375031
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.01.027
SAMP1/YitFc mice develop ileitis via loss of CCL21 and defects in dendritic cell migration
Abstract
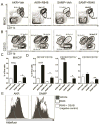
Background & aims: The lymphatic chemokine CCL21 is required for dendritic cell (DC) migration from tissues to lymph nodes, which helps establish tolerance to foreign yet harmless antigens. We demonstrate that CCL21 is almost completely absent from SAMP1/YitFc (SAMP) mice, which spontaneously develop chronic ileitis that resembles Crohn's disease, and that DC migration is severely impaired in these mice compared with AKR mice (controls). Toll-like receptor agonists like the Toll-like receptor 7 agonist R848 induce DC maturation and mobilization.
Methods: We collected intestinal and other tissues and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) from SAMP mice. Expression of CCL21 was measured by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence analyses; spontaneous and induced migration of DCs were assessed by flow cytometry. We analyzed production of retinoic acid by DCs and their ability to induce development of regulatory T cells. Mice were fed R848 to determine its effects on migration of DCs and development of ileitis in SAMP mice.
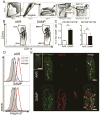
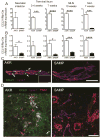
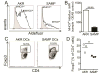
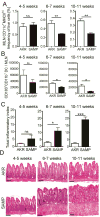
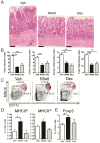
Results: SAMP mice expressed almost no CCL21 in any tissue tested. Their CD11b(+)CD103(+) DCs were defective in migration from the ileal lamina propria to the MLN. DCs from SAMP mice also had a greatly reduced ability to produce retinoic acid and induce development of regulatory T cells compared with control mice. Young SAMP mice had reduced CCL21 expression and decreased DC migration before developing ileitis. Administration of R848 to adult SAMP mice increased migration of DC to the MLN and development of regulatory T cells there, and reduced the severity of ileitis.
Conclusions: Loss of CCL21 signaling and DC migration is required for development of ileitis in SAMP mice. Reagents such as R848, which activate DC migration to the MLN, may be developed as treatments for patients with Crohn's disease.
Keywords: CD; Immune Regulation; Oral Tolerance; Small Intestine.
Copyright © 2015 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

