Cortical inputs to the middle temporal visual area in New World owl monkeys
- PMID: 25620872
- PMCID: PMC4302954
- DOI: 10.2147/EB.S69713
Cortical inputs to the middle temporal visual area in New World owl monkeys
Abstract
We made eight retrograde tracer injections into the middle temporal visual area (MT) of three New World owl monkeys (Aotus nancymaae). These injections were placed across the representation of the retina in MT to allow us to compare the locations of labeled cells in other areas in order to provide evidence for any retinotopic organization in those areas. Four regions projected to MT: 1) early visual areas, including V1, V2, V3, the dorsolateral visual area, and the dorsomedial visual area, provided topographically organized inputs to MT; 2) all areas in the MT complex (the middle temporal crescent, the middle superior temporal area, and the fundal areas of the superior temporal sulcus) projected to MT. Somewhat variably across injections, neurons were labeled in other parts of the temporal lobe; 3) regions in the location of the medial visual area, the posterior parietal cortex, and the lateral sulcus provided other inputs to MT; 4) finally, projections from the frontal eye field, frontal visual field, and prefrontal cortex were also labeled by our injections. These results further establish the sources of input to MT, and provide direct evidence within and across cases for retinotopic patterns of projections from early visual areas to MT.
Keywords: middle temporal area; parietal cortex; visual cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

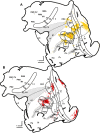

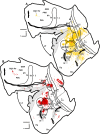
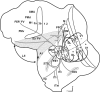
Similar articles
-
Cortical connections of the dorsomedial visual area in new world owl monkeys (Aotus trivirgatus) and squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus).J Comp Neurol. 1998 Oct 12;400(1):18-34. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19981012)400:1<18::aid-cne2>3.0.co;2-w. J Comp Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9762864
-
Cortical connections of the middle temporal visual area (MT) and the superior temporal cortex in owl monkeys.J Comp Neurol. 1984 Sep 1;228(1):81-104. doi: 10.1002/cne.902280109. J Comp Neurol. 1984. PMID: 6480909
-
Cortical afferents of visual area MT in the Cebus monkey: possible homologies between New and Old World monkeys.Vis Neurosci. 1993 Sep-Oct;10(5):827-55. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800006064. Vis Neurosci. 1993. PMID: 8217935
-
Cortical connections of MT in four species of primates: areal, modular, and retinotopic patterns.Vis Neurosci. 1990 Aug;5(2):165-204. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800000213. Vis Neurosci. 1990. PMID: 2278944 Review.
-
Cortical connections of the middle temporal and the middle temporal crescent visual areas in prosimian galagos (Otolemur garnetti).Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2007 Mar;290(3):349-66. doi: 10.1002/ar.20440. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2007. PMID: 17525950
Cited by
-
Transient visual pathway critical for normal development of primate grasping behavior.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 6;115(6):1364-1369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717016115. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29298912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allman JM, Kaas JH. A representation of the visual field in the caudal third of the middle temporal gyrus of the owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus) Brain Res. 1971;31(1):85–105. - PubMed
-
- Allman JM, Kaas JH. Representation of the visual field in striate and adjoining cortex of the owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus) Brain Res. 1971;35(1):89–106. - PubMed
-
- Allman JM, Kaas JH, Lane RH. The middle temporal visual area (MT) in the bushbaby, Galago senegalensis. Brain Res. 1973;57(1):197–202. - PubMed
-
- Malonek D, Tootell RB, Grinvald A. Optical imaging reveals the functional architecture of neurons processing shape and motion in owl monkey area MT. Proc Biol Sci. 1994;258(1352):109–119. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

