Lupus risk variants in the PXK locus alter B-cell receptor internalization
- PMID: 25620976
- PMCID: PMC4288052
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00450
Lupus risk variants in the PXK locus alter B-cell receptor internalization
Abstract
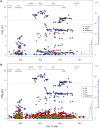
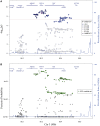
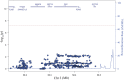
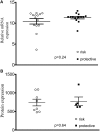
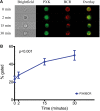
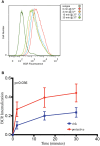
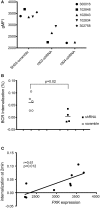
Genome wide association studies have identified variants in PXK that confer risk for humoral autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus), rheumatoid arthritis and more recently systemic sclerosis. While PXK is involved in trafficking of epidermal growth factor Receptor (EGFR) in COS-7 cells, mechanisms linking PXK to lupus pathophysiology have remained undefined. In an effort to uncover the mechanism at this locus that increases lupus-risk, we undertook a fine-mapping analysis in a large multi-ancestral study of lupus patients and controls. We define a large (257kb) common haplotype marking a single causal variant that confers lupus risk detected only in European ancestral populations and spans the promoter through the 3' UTR of PXK. The strongest association was found at rs6445972 with P < 4.62 × 10(-10), OR 0.81 (0.75-0.86). Using stepwise logistic regression analysis, we demonstrate that one signal drives the genetic association in the region. Bayesian analysis confirms our results, identifying a 95% credible set consisting of 172 variants spanning 202 kb. Functionally, we found that PXK operates on the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR); we confirmed that PXK influenced the rate of BCR internalization. Furthermore, we demonstrate that individuals carrying the risk haplotype exhibited a decreased rate of BCR internalization, a process known to impact B cell survival and cell fate. Taken together, these data define a new candidate mechanism for the genetic association of variants around PXK with lupus risk and highlight the regulation of intracellular trafficking as a genetically regulated pathway mediating human autoimmunity.
Keywords: B cells; BCR; PXK; fine-mapping; lupus.
Figures
References
-
- Alhouayek M., Masquelier J., Cani P. D., Lambert D. M., Muccioli G. G. (2013). Implication of the anti-inflammatory bioactive lipid prostaglandin D2-glycerol ester in the control of macrophage activation and inflammation by ABHD6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 17558–17563. 10.1073/pnas.1314017110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- P60 AR053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104938/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR065626/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK078392/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM063483/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001834/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI078004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK090971/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR047363/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR062755/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

