Hearing outcome after type I tympanoplasty: a retrospective study
- PMID: 25621230
- PMCID: PMC4298574
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-014-0749-8
Hearing outcome after type I tympanoplasty: a retrospective study
Abstract
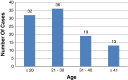
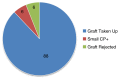
The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the hearing outcomes using temporalis fascia graft for tympanic membrane reconstruction in type 1 tympanoplasty. It included 100 patients with tubotympanic type of chronic suppurative otitis media requiring only tympanic membrane reconstruction. Patients requiring ossicular reconstruction or with attico antral disease were excluded. Patients were assessed after 3, 6 months and 1 year for graft status and hearing outcome. Hearing evaluation was done using tuning fork tests and pure tone audiometry. In total, 88 out of 100 patients had intact and completely healed grafts at 1 year postoperatively (success rate of 88 %). The Hearing gain achieved was 14.55 dBs and the mean air bone gap reduction was 11.94 dBs. This reduction was statistically significant when compared to the pre operative hearing conditions.
Keywords: Post aural approach; Temporalis fascia; Type 1 tympanoplasty; Underlay technique.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcome of Type 1 Tympanoplasty in Al Nahdha Hospital and Influencing Factors: A Retrospective Study.Oman Med J. 2024 Sep 30;39(5):e675. doi: 10.5001/omj.2024.106. eCollection 2024 Sep. Oman Med J. 2024. PMID: 40070807 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Type 1 Tympanoplasty on the Quality of Life of CSOM Patients.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Dec;68(4):468-474. doi: 10.1007/s12070-016-0989-x. Epub 2016 May 9. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 27833874 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between clinical and audiological results of tympanoplasty with modified sandwich technique and underlay technique.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 May-Jun;84(3):318-323. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 28476655 Free PMC article.
-
Fascia compared to one-piece composite cartilage-perichondrium grafting for tympanoplasty.Laryngoscope. 2016 Jul;126(7):1662-70. doi: 10.1002/lary.25772. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Laryngoscope. 2016. PMID: 26542167 Review.
-
Comparison of cartilage with temporalis fascia tympanoplasty: A meta-analysis of comparative studies.Laryngoscope. 2017 Sep;127(9):2139-2148. doi: 10.1002/lary.26451. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Laryngoscope. 2017. PMID: 27933630 Review.
Cited by
-
Outcome of Type 1 Tympanoplasty in Al Nahdha Hospital and Influencing Factors: A Retrospective Study.Oman Med J. 2024 Sep 30;39(5):e675. doi: 10.5001/omj.2024.106. eCollection 2024 Sep. Oman Med J. 2024. PMID: 40070807 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Sacrificing Tensor Tympani Muscle Tendon When Manubrium of Malleus Is Foreshortened in Type I Tympanoplasty.Int J Otolaryngol. 2015;2015:531296. doi: 10.1155/2015/531296. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Int J Otolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 26697069 Free PMC article.
-
Indian Perspectives on Graft Materials Used for Repair of Tympanic Membrane.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Jul;11(7):ME01-ME06. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/26289.10199. Epub 2017 Jul 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 28892946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Degree of Hearing Improvement and Reduction of Air-Bone Gap After Tympanoplasty in a Tertiary Hospital in Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2024 Feb 28;16(2):e55159. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55159. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38558666 Free PMC article.
-
Global surgery in a postconflict setting--5-year results of implementation in the Russian North Caucasus.Glob Health Action. 2015 Oct 23;8:29227. doi: 10.3402/gha.v8.29227. eCollection 2015. Glob Health Action. 2015. PMID: 26498745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Browning GG et al Scott-brown’s otorhinolaryngology head and neck surgery, 7th edn. 3:3421
-
- Khan NA. Repair of traumatic perforation of tympanic membranes by a new technique. Pak J Otolaryngol. 1992;8:177–179.
-
- Javed M, Khan S, Ullah H, Shah J. Onlay versus underlay myringoplasty, audiological results. Pak J Otolaryngol. 2000;16:59–60.
-
- Ashfaq M, Aasim MU, Khan N. Myringoplasty: anatomical and functional results. Pak Armed Forces Med J. 2004;54(2):155–158.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous