Sentinel lymph node localization using 1 % isosulfan blue dye in cases of early oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25621255
- PMCID: PMC4298623
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-014-0752-0
Sentinel lymph node localization using 1 % isosulfan blue dye in cases of early oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
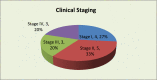
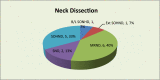
To study the use of 1 % isosulfan blue dye in identifying sentinel node, sensitivity and specificity of frozen section and predictive value of sentinel node in predicting other nodal status in the cases of oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 15 patients of oral cavity and oropharyngeal SCC with clinically N0 neck, who required WLE of the primary lesion as well as neck dissection as per recommended treatment protocol, were selected from OPD. 1 % Isosulfan dye was injected peritumorally intraoperatively after the induction of general anaesthesia. Neck dissection was performed and first node taking up the blue dye was identified, dissected, removed and was sent for frozen section. In two of the 15 cases a sentinel node was identified (sensitivity of the technique-13 %). Both the sentinel nodes were positive for presence of metastasis on final histopathology (specificity-100 %). However, five cases had nodal metastasis on final histopathological examination of the neck dissection specimen (sensitivity of sentinel lymph node biopsy-40 %). Frozen section examination had a sensitivity and specificity of 100 %. All data was analyzed using SPSS 16 software. Use of 1 % Isosulfan Dye for identification of sentinel node is a simple and cheap technique, however, it has low sensitivity as compared to the use of triple diagnostic procedure consisting of lymphoscintigraphy, per op gamma probe localization and using isosulfan dye for sentinel node identification. Sentinel lymph node is representative of nodal status and correlates well with the final histopathological examination of the dissected neck nodes.
Keywords: Frozen section; Isosulfan blue dye; N0 neck; SLNB (sentinel lymph node biopsy); Sentinel node.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Evaluation in Early Stage T1, T2, N0, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity with Methylene Blue Dye.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2025 Feb;16(1):245-250. doi: 10.1007/s13193-024-02078-7. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40114874
-
Sentinel lymph node biopsy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Laryngoscope. 2002 Dec;112(12):2101-13. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200212000-00001. Laryngoscope. 2002. PMID: 12461328
-
The application of sentinel node radiolocalization to solid tumors of the head and neck: a 10-year experience.Laryngoscope. 2004 Jan;114(1):2-19. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200401000-00002. Laryngoscope. 2004. PMID: 14709988 Review.
-
Role of methylene blue dye in sentinel node biopsy in N0 oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma.Indian J Cancer. 2024 Jan 1;61(1):22-28. doi: 10.4103/ijc.IJC_862_20. Epub 2023 Dec 3. Indian J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38078458
-
Clinical practice guidelines for the use of axillary sentinel lymph node biopsy in carcinoma of the breast: current update.Breast J. 2004 Mar-Apr;10(2):85-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1075-122x.2004.21439.x. Breast J. 2004. PMID: 15009032 Review.
Cited by
-
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Evaluation in Early Stage T1, T2, N0, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity with Methylene Blue Dye.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2025 Feb;16(1):245-250. doi: 10.1007/s13193-024-02078-7. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40114874
References
-
- Wiseman SM, Loree TR, Hicks WL, Rigual NR. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in SCC of the head and neck: a major advance in staging the N0 neck. ENT-Ear Nose Throat J. 2002;81(3):156–163. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous