Clinicopathological review and survival characteristics of adenoid cystic carcinoma
- PMID: 25621256
- PMCID: PMC4298605
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-014-0755-x
Clinicopathological review and survival characteristics of adenoid cystic carcinoma
Abstract
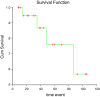
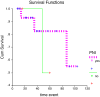
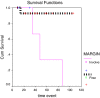
To study the clinical characters, the outcomes of treatments and the factors affecting treatment results of adenoid cystic carcinomas at Shahid Sadoughi Hospital and Shahid Ramazanzadeh radiotherapy center, Yazd, Iran. The clinical data of 31 patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma of any anatomic site diagnosed over an 8 year period (2004-2012), were investigated retrospectively. Data regarding patients' characteristics, pathological features and follow-up were obtained from patients records. Survival rate, local recurrence and distant metastasis were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method. Prognosis factors were analyzed by Log-rank test and Cox regression. The study included31 patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma. The mean age at presentation was 50.2 ± 24.8 years. There were 11 (35.5 %) males and 20 (64.5 %) females with a female predilection (M:F = 0.55:1). Parotid gland was the most common site (8/31, 25.7 %) followed by submandibular gland (7/31, 22.6 %). Perineural invasion was detected in 67.7 % of the cases. Positive surgical status was reported in 48.4 % of the specimens. Metastasis was detected in 25.8 % of the patients and the most common site of distant metastasis was lung. Overall survival rates at 2, 5, and 7 years were 95, 75, and 57 % respectively. Margin status showed significant effect on survival (P value = 0.01). Positive surgical margin is an important factor affecting the prognosis of the patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma. Surgery with negative surgical margin is the first choice of treatment for the patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma. Our findings show that the prognosis of patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma in our center is fair.
Keywords: Adenoid cystic carcinoma; Clinicopathology; Survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Prognostic analysis of adenoid cystic carcinoma of major salivary glands of 64 cases].Ai Zheng. 2006 Sep;25(9):1138-43. Ai Zheng. 2006. PMID: 16965658 Chinese.
-
Intraoral adenoid cystic carcinoma: prognostic factors and outcome.Oral Oncol. 2008 Oct;44(10):986-93. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2008.01.004. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Oral Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18329324
-
[Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck: a retrospective series of 169 cases].Cancer Radiother. 2012 Jul-Aug;16(4):247-56. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2012.02.003. Epub 2012 May 29. Cancer Radiother. 2012. PMID: 22652299 French.
-
Adenoid cystic carcinoma: a retrospective clinical review.Int J Cancer. 2001 Jun 20;96(3):149-58. doi: 10.1002/ijc.1013. Int J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11410883 Review.
-
Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands: a review of 10 years.Laryngoscope. 1997 Sep;107(9):1276-80. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199709000-00022. Laryngoscope. 1997. PMID: 9292617 Review.
Cited by
-
PSMA-Directed Imaging and Therapy of Salivary Gland Tumors: A Single-Center Retrospective Study.J Nucl Med. 2023 Mar;64(3):372-378. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264342. Epub 2022 Sep 22. J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 36137757 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Intraosseous Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma with Widespread Skeletal Metastases Showing Features of High-Grade Transformation.Head Neck Pathol. 2021 Jun;15(2):715-722. doi: 10.1007/s12105-020-01228-x. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Head Neck Pathol. 2021. PMID: 32959213 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic effects of surgery or radiotherapy on adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck: a retrospective cohort study.Gland Surg. 2022 Nov;11(11):1784-1794. doi: 10.21037/gs-22-526. Gland Surg. 2022. PMID: 36518804 Free PMC article.
-
A torus-like sublingual adenoid cystic carcinoma in a 35-year-old male: Review of literature and case report.Clin Case Rep. 2023 Jul 18;11(7):e7591. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.7591. eCollection 2023 Jul. Clin Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37476597 Free PMC article.
-
Liver metastasis as the initial clinical manifestation of sublingual gland adenoid cystic carcinoma: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Jul 6;9(19):5238-5244. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5238. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 34307573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eveson J, Nagao TW. Diseases of the salivary glands. In: Barnes L, editor. Surgical pathology of the head and neck. 3. New York: Informa Healthcare; 2009. pp. 552–557.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources