Whole genome sequencing and analysis reveal insights into the genetic structure, diversity and evolutionary relatedness of luxI and luxR homologs in bacteria belonging to the Sphingomonadaceae family
- PMID: 25621282
- PMCID: PMC4288048
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00188
Whole genome sequencing and analysis reveal insights into the genetic structure, diversity and evolutionary relatedness of luxI and luxR homologs in bacteria belonging to the Sphingomonadaceae family
Abstract
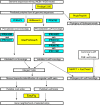
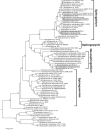
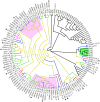
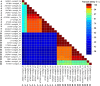
Here we report the draft genomes and annotation of four N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL)-producing members from the family Sphingomonadaceae. Comparative genomic analyses of 62 Sphingomonadaceae genomes were performed to gain insights into the distribution of the canonical luxI/R-type quorum sensing (QS) network within this family. Forty genomes contained at least one luxR homolog while the genome of Sphingobium yanoikuyae B1 contained seven Open Reading Frames (ORFs) that have significant homology to that of luxR. Thirty-three genomes contained at least one luxI homolog while the genomes of Sphingobium sp. SYK6, Sphingobium japonicum, and Sphingobium lactosutens contained four luxI. Using phylogenetic analysis, the sphingomonad LuxR homologs formed five distinct clades with two minor clades located near the plant associated bacteria (PAB) LuxR solo clade. This work for the first time shows that 13 Sphingobium and one Sphingomonas genome(s) contain three convergently oriented genes composed of two tandem luxR genes proximal to one luxI (luxR-luxR-luxI). Interestingly, luxI solos were identified in two Sphingobium species and may represent species that contribute to AHL-based QS system by contributing AHL molecules but are unable to perceive AHLs as signals. This work provides the most comprehensive description of the luxI/R circuitry and genome-based taxonomical description of the available sphingomonad genomes to date indicating that the presence of luxR solos and luxI solos are not an uncommon feature in members of the Sphingomonadaceae family.
Keywords: Novosphingobium; Sphingomonadaceae; luxI/R; luxR solos; phylogenetic; quorum-sensing; whole genome sequencing.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Census of solo LuxR genes in prokaryotic genomes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Mar 12;5:20. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00020. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25815274 Free PMC article.
-
LuxR solos in Photorhabdus species.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Nov 18;4:166. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00166. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25478328 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of LuxI and LuxR Protein Homologs of N-Acylhomoserine Lactone-Dependent Quorum Sensing System in Pseudoalteromonas sp. 520P1.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017 Feb;19(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s10126-016-9726-4. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017. PMID: 28083715
-
An evolving perspective on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum sensing regulator QscR.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Oct 28;4:152. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00152. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25389523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances in quorum-sensing LuxR solos in bacteria].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2017 Mar 4;57(3):341-9. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 29756433 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Improved genome of Agrobacterium radiobacter type strain provides new taxonomic insight into Agrobacterium genomospecies 4.PeerJ. 2019 Feb 8;7:e6366. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6366. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30775173 Free PMC article.
-
In silico Analysis Reveals Distribution of Quorum Sensing Genes and Consistent Presence of LuxR Solos in the Pandoraea Species.Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 6;10:1758. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01758. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31447806 Free PMC article.
-
Genome mining identifies cepacin as a plant-protective metabolite of the biopesticidal bacterium Burkholderia ambifaria.Nat Microbiol. 2019 Jun;4(6):996-1005. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0383-z. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Nat Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30833726 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing-assisted identification and the first functional validation of N-acyl-homoserine-lactone synthases from the Sphingomonadaceae family.PeerJ. 2016 Aug 30;4:e2332. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2332. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27635318 Free PMC article.
-
Insight Into the Microbial Co-occurrence and Diversity of 73 Grapevine (Vitis vinifera) Crown Galls Collected Across the Northern Hemisphere.Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 13;10:1896. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01896. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31456792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aylward F. O., McDonald B. R., Adams S. M., Valenzuela A., Schmidt R. A., Goodwin L. A., et al. . (2013). Comparison of 26 sphingomonad genomes reveals diverse environmental adaptations and biodegradative capabilities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79, 3724–3733. 10.1128/AEM.00518-13 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

