Altered Cholesterol Intracellular Trafficking and the Development of Pathological Hallmarks of Sporadic AD
- PMID: 25621310
- PMCID: PMC4302957
- DOI: 10.13188/2376-922x.1000002
Altered Cholesterol Intracellular Trafficking and the Development of Pathological Hallmarks of Sporadic AD
Abstract
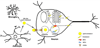
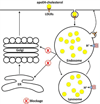
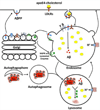
Compared to the rare familial early onset Alzheimer's disease (AD) that results from gene mutations in AbPP and presenilin-1, the pathogenesis of sporadic AD is much more complex and is believed to result from complex interactions between nutritional, environmental, epigenetic and genetic factors. Among those factors, the presence APOE4 is still the single strongest genetic risk factor for sporadic AD. However, the exact underlying mechanism whereby apoE4 contributes to the pathogenesis of sporadic AD remains unclear. Here, we discuss how altered cholesterol intracellular trafficking as a result of apoE4 might contribute to the development of pathological hallmarks of AD including brain deposition of amyloid beta (Ab), neurofibrillary tangles, and synaptic dysfunction.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; ApoE4; Cholesterol; Niemann-Pick type C disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein gene and its interaction with the environmentally driven risk factors: molecular, genetic and epidemiological studies of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2004 May-Jun;25(5):651-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.12.024. Neurobiol Aging. 2004. PMID: 15172744
-
Role of LDL cholesterol and endolysosomes in amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer's disease.J Neurol Neurophysiol. 2014 Oct 1;5(5):236. doi: 10.4172/2155-9562.1000236. J Neurol Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 26413387 Free PMC article.
-
New insight into the role of altered brain cholesterol metabolism in the pathogenesis of AD: A unifying cholesterol hypothesis and new therapeutic approach for AD.Brain Res Bull. 2025 May;224:111321. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2025.111321. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 40164234 Review.
-
Streptozotocin Intracerebroventricular-Induced Neurotoxicity and Brain Insulin Resistance: a Therapeutic Intervention for Treatment of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease (sAD)-Like Pathology.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Sep;53(7):4548-62. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9384-y. Epub 2015 Aug 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26298663 Review.
-
Intracellular Trafficking Mechanisms of Synaptic Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Apr 17;14:72. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00072. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32362813 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Amyloid-beta Alzheimer targets - protein processing, lipid rafts, and amyloid-beta pores.Yale J Biol Med. 2016 Mar 24;89(1):5-21. eCollection 2016 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27505013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocytic Propagation of Tau in the Context of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Mar 17;15:645233. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.645233. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33815065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards a Unitary Hypothesis of Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;98(4):1243-1275. doi: 10.3233/JAD-231318. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38578892 Free PMC article.
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induces signs of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in wild-type mice and accelerates pathological signs of AD in an AD model.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Jan 5;13:1. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0467-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 26728181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glenner GG, Wong CW. Alzheimer’s disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;120:885–890. - PubMed
-
- Goate A, Hardy J. Twenty years of Alzheimer’s disease-causing mutations. J Neurochem. 2011;120(Suppl 1):3–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
