Cleavage efficient 2A peptides for high level monoclonal antibody expression in CHO cells
- PMID: 25621616
- PMCID: PMC4622431
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1008351
Cleavage efficient 2A peptides for high level monoclonal antibody expression in CHO cells
Abstract
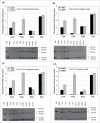
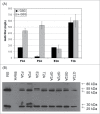
Linking the heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC) genes required for monoclonal antibodies (mAb) production on a single cassette using 2A peptides allows control of LC and HC ratio and reduces non-expressing cells. Four 2A peptides derived from the foot-and-mouth disease virus (F2A), equine rhinitis A virus (E2A), porcine teschovirus-1 (P2A) and Thosea asigna virus (T2A), respectively, were compared for expression of 3 biosimilar IgG1 mAbs in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines. HC and LC were linked by different 2A peptides both in the absence and presence of GSG linkers. Insertion of a furin recognition site upstream of 2A allowed removal of 2A residues that would otherwise be attached to the HC. Different 2A peptides exhibited different cleavage efficiencies that correlated to the mAb expression level. The relative cleavage efficiency of each 2A peptide remains similar for expression of different IgG1 mAbs in different CHO cells. While complete cleavage was not observed for any of the 2A peptides, GSG linkers did enhance the cleavage efficiency and thus the mAb expression level. T2A with the GSG linker (GT2A) exhibited the highest cleavage efficiency and mAb expression level. Stably amplified CHO DG44 pools generated using GT2A had titers 357, 416 and 600 mg/L for the 3 mAbs in shake flask batch cultures. Incomplete cleavage likely resulted in incorrectly processed mAb species and aggregates, which were removed with a chromatin-directed clarification method and protein A purification. The vector and methods presented provide an easy process beneficial for both mAb development and manufacturing.
Keywords: 2A peptide; CHO; CHO, Chinese hamster ovary; E2A, 2A peptide derived from the equine rhinitis virus; F2A, 2A peptide derived from the foot-and-mouth disease virus; G, glycine; GE2A, E2A with the GSG linker; GF2A, F2A with the GSG linker; GFP, green fluorescence protein; GP2A, P2A with the GSG linker; GSG linker; GT2A, T2A with the GSG linker; HC, heavy chain; HT, hypoxanthine and thymine; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; IgG, immunoglobulin G; K, lysine; LC, light chain; MS, mass spectrometry; MTX, methotrexate; P, proline; P2A, 2A peptide derived from the porcine teschovirus-1; PFM, protein-free medium; PVDF, polyvinylidene difluoride; SEC, size exclusion chromatography; T2A, 2A peptide derived from the Thosea asigna virus; cleavage efficiency; furin; mAb, monoclonal antibody; monoclonal antibody.
Figures




References
-
- Nelson AL, Dhimolea E, Reichert JM. Development trends for human monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010; 9:767-74; PMID:20811384; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrd3229 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ho SCL, Tong YW, Yang YS. Generation of monoclonal antibody-producing mammalian cell lines. Pharmaceut Bioprocess 2013; 1:71-87; http://dx.doi.org/10.4155/pbp.13.8 - DOI
-
- Birch JR, Racher AJ. Antibody production. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2006; 58:671-85; PMID:16822577; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2005.12.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barnes LM, Bentley CM, Moy N, Dickson AJ. Molecular analysis of successful cell line selection in transfected GS-NS0 myeloma cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 2007; 96:337-48; PMID:17001634; http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bit.21119 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ng SK, Lin W, Sachdeva R, Wang DI, Yap MG. Vector fragmentation: characterizing vector integrity in transfected clones by Southern blotting. Biotechnol Prog 2010; 26:11-20; PMID:19847885; http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/btpr.281 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
