Diseases of pulmonary surfactant homeostasis
- PMID: 25621661
- PMCID: PMC4316199
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104644
Diseases of pulmonary surfactant homeostasis
Abstract
Advances in physiology and biochemistry have provided fundamental insights into the role of pulmonary surfactant in the pathogenesis and treatment of preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Identification of the surfactant proteins, lipid transporters, and transcriptional networks regulating their expression has provided the tools and insights needed to discern the molecular and cellular processes regulating the production and function of pulmonary surfactant prior to and after birth. Mutations in genes regulating surfactant homeostasis have been associated with severe lung disease in neonates and older infants. Biophysical and transgenic mouse models have provided insight into the mechanisms underlying surfactant protein and alveolar homeostasis. These studies have provided the framework for understanding the structure and function of pulmonary surfactant, which has informed understanding of the pathogenesis of diverse pulmonary disorders previously considered idiopathic. This review considers the pulmonary surfactant system and the genetic causes of acute and chronic lung disease caused by disruption of alveolar homeostasis.
Keywords: alveolar capillary dysplasia; alveolar proteinosis; interstitial lung disease; pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis; pulmonary fibrosis; respiratory distress syndrome.
Figures
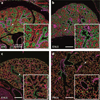
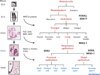
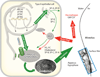
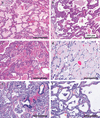
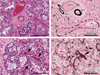
References
-
- Kimura S, Hara Y, Pineau T, Fernandez-Salguero P, Fox CH, et al. The T/ebp null mouse: thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein is essential for the organogenesis of the thyroid, lung, ventral forebrain, and pituitary. Genes Dev. 1996;10:60–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

