Interactions of amino acid side-chain analogs within membrane environments
- PMID: 25621811
- PMCID: PMC4420737
- DOI: 10.1021/jp511712u
Interactions of amino acid side-chain analogs within membrane environments
Abstract
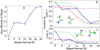
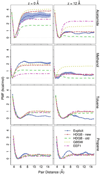
The interactions among four amino acid analog pairs (Asn, Ser, Phe, and Val) within the membrane environment were investigated using umbrella sampling molecular dynamics simulations. The results confirm generally expected qualitative trends of preferential association of polar compounds inside the membrane vs preferential interaction of hydrophobic compounds outside the membrane. Furthermore, correlations between amino acid interactions, membrane insertion, and membrane deformations are discussed and a detailed analysis of pair interaction energies is presented. A comparison of the energetics obtained from explicit lipid simulations with those from implicit membrane models reveals significant deviations and an improved parametrization of the heterogeneous dielectric generalized Born implicit model is provided that partially corrects for deficiencies in the implicit membrane model when compared with the new reference data from this study.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydration free energies of amino acids: why side chain analog data are not enough.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Jul 2;113(26):8967-74. doi: 10.1021/jp902638y. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19507836
-
Potentials of mean force between ionizable amino acid side chains in water.J Am Chem Soc. 2003 Feb 19;125(7):1722-30. doi: 10.1021/ja025521w. J Am Chem Soc. 2003. PMID: 12580597
-
Thermodynamic stability of hydrogen-bonded systems in polar and nonpolar environments.J Comput Chem. 2010 Jul 30;31(10):2046-55. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21491. J Comput Chem. 2010. PMID: 20127744
-
The importance of membrane defects-lessons from simulations.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Aug 19;47(8):2244-51. doi: 10.1021/ar4002729. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24892900
-
Membrane proteins: molecular dynamics simulations.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Aug;18(4):425-31. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.02.003. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18406600 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure refinement of membrane proteins via molecular dynamics simulations.Proteins. 2018 Jul;86(7):738-750. doi: 10.1002/prot.25508. Epub 2018 May 6. Proteins. 2018. PMID: 29675899 Free PMC article.
-
Discrimination of Native-like States of Membrane Proteins with Implicit Membrane-based Scoring Functions.J Chem Theory Comput. 2017 Jun 13;13(6):3049-3059. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.7b00254. Epub 2017 May 11. J Chem Theory Comput. 2017. PMID: 28475346 Free PMC article.
-
Generalized Born Implicit Solvent Models for Biomolecules.Annu Rev Biophys. 2019 May 6;48:275-296. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-052118-115325. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Annu Rev Biophys. 2019. PMID: 30857399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous dielectric generalized Born model with a van der Waals term provides improved association energetics of membrane-embedded transmembrane helices.J Comput Chem. 2017 Jun 15;38(16):1308-1320. doi: 10.1002/jcc.24691. Epub 2017 Feb 4. J Comput Chem. 2017. PMID: 28160300 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Prediction of the Binding, Folding, Insertion, and Overall Stability of Membrane-Active Peptides.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2315:161-182. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1468-6_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34302676
References
-
- Bennett WFD, Tieleman DP. Computer simulations of lipid membrane domains. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 2013;1828(8):1765–1776. - PubMed
-
- Andersen OS, Koeppe RE. Bilayer Thickness and Membrane Protein Function: An Energetic Perspective. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 2007;36(1):107–130. - PubMed
-
- Marrink SJ, Risselada HJ, Yefimov S, Tieleman DP, de Vries AH. The MARTINI force field: Coarse grained model for biomolecular simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2007;111(27):7812–7824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

