Directed evolution combined with synthetic biology strategies expedite semi-rational engineering of genes and genomes
- PMID: 25621864
- PMCID: PMC4601291
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2015.1011029
Directed evolution combined with synthetic biology strategies expedite semi-rational engineering of genes and genomes
Abstract
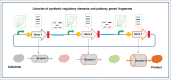
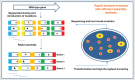
Owing to our limited understanding of the relationship between sequence and function and the interaction between intracellular pathways and regulatory systems, the rational design of enzyme-coding genes and de novo assembly of a brand-new artificial genome for a desired functionality or phenotype are difficult to achieve. As an alternative approach, directed evolution has been widely used to engineer genomes and enzyme-coding genes. In particular, significant developments toward DNA synthesis, DNA assembly (in vitro or in vivo), recombination-mediated genetic engineering, and high-throughput screening techniques in the field of synthetic biology have been matured and widely adopted, enabling rapid semi-rational genome engineering to generate variants with desired properties. In this commentary, these novel tools and their corresponding applications in the directed evolution of genomes and enzymes are discussed. Moreover, the strategies for genome engineering and rapid in vitro enzyme evolution are also proposed.
Keywords: DNA assembly; HTS, high-throughput screening; LCR, Ligase Cycling Reaction; MAGE, multiplex automated genome engineering; directed evolution; dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; enzyme; genome engineering; metabolic engineering; recombineering; ssDNA, single-stranded DNA; synthetic biology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polishing the craft of genetic diversity creation in directed evolution.Biotechnol Adv. 2013 Dec;31(8):1707-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.08.021. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Biotechnol Adv. 2013. PMID: 24012599 Review.
-
Multiplexed genome engineering and genotyping methods applications for synthetic biology and metabolic engineering.Methods Enzymol. 2011;498:409-26. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385120-8.00018-8. Methods Enzymol. 2011. PMID: 21601688
-
Design Methodologies and the Limits of the Engineering-Dominated Conception of Synthetic Biology.Acta Biotheor. 2019 Mar;67(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s10441-018-9338-7. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Acta Biotheor. 2019. PMID: 30121875
-
Combinatorial Evolution of DNA with RECODE.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1772:205-212. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7795-6_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29754230
-
From molecular engineering to process engineering: development of high-throughput screening methods in enzyme directed evolution.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jan;102(2):559-567. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8568-y. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29181567 Review.
Cited by
-
Scarless assembly of unphosphorylated DNA fragments with a simplified DATEL method.Bioengineered. 2017 May 4;8(3):296-301. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2017.1308986. Bioengineered. 2017. PMID: 28384080 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Calcium Detection Methods in Animal Systems: A Sandbox for Synthetic Biology.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 24;11(3):343. doi: 10.3390/biom11030343. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33668387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production of novel NaN3-resistant creatine amidinohydrolase in recombinant Escherichia coli.Bioengineered. 2015;6(4):248-50. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2015.1052919. Bioengineered. 2015. PMID: 26083084 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of the Clostridium difficile LCL126.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):745-754. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1894798. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 33896381 Free PMC article.
-
Transition of Eocene whales from land to sea: evidence from bone microstructure.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 25;10(2):e0118409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118409. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25714394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2000; 28:27-30; PMID:10592173; http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hibbert EG, Baganz F, Hailes HC, Ward JM, Lye GJ, Woodley JM, Dalby PA. Directed evolution of biocatalytic processes. Biomol Eng 2005; 22:11-9; PMID:15857779; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bioeng.2004.09.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Turner NJ. Directed evolution drives the next generation of biocatalysts. Nat Chem Biol 2009; 5:567-73; PMID:19620998; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.203 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cobb RE, Si T, Zhao H. Directed evolution: an evolving and enabling synthetic biology tool. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2012; 16:285-91; PMID:22673064; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.05.186 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dalby PA. Strategy and success for the directed evolution of enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2011; 21:473-80; PMID:21684150; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2011.05.003 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
