Performance of genotype imputation for low frequency and rare variants from the 1000 genomes
- PMID: 25621886
- PMCID: PMC4306552
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116487
Performance of genotype imputation for low frequency and rare variants from the 1000 genomes
Abstract
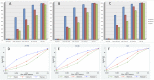
Genotype imputation is now routinely applied in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and meta-analyses. However, most of the imputations have been run using HapMap samples as reference, imputation of low frequency and rare variants (minor allele frequency (MAF) < 5%) are not systemically assessed. With the emergence of next-generation sequencing, large reference panels (such as the 1000 Genomes panel) are available to facilitate imputation of these variants. Therefore, in order to estimate the performance of low frequency and rare variants imputation, we imputed 153 individuals, each of whom had 3 different genotype array data including 317k, 610k and 1 million SNPs, to three different reference panels: the 1000 Genomes pilot March 2010 release (1KGpilot), the 1000 Genomes interim August 2010 release (1KGinterim), and the 1000 Genomes phase1 November 2010 and May 2011 release (1KGphase1) by using IMPUTE version 2. The differences between these three releases of the 1000 Genomes data are the sample size, ancestry diversity, number of variants and their frequency spectrum. We found that both reference panel and GWAS chip density affect the imputation of low frequency and rare variants. 1KGphase1 outperformed the other 2 panels, at higher concordance rate, higher proportion of well-imputed variants (info>0.4) and higher mean info score in each MAF bin. Similarly, 1M chip array outperformed 610K and 317K. However for very rare variants (MAF ≤ 0.3%), only 0-1% of the variants were well imputed. We conclude that the imputation of low frequency and rare variants improves with larger reference panels and higher density of genome-wide genotyping arrays. Yet, despite a large reference panel size and dense genotyping density, very rare variants remain difficult to impute.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of genome-wide genotyping and reference panels on rare variants imputation.J Genet Genomics. 2012 Oct 20;39(10):545-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Jul 24. J Genet Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23089364
-
Comprehensive evaluation of imputation performance in African Americans.J Hum Genet. 2012 Jul;57(7):411-21. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2012.43. Epub 2012 May 31. J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22648186 Free PMC article.
-
Improving accuracy of rare variant imputation with a two-step imputation approach.Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 Mar;23(3):395-400. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.91. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 24939589 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype Imputation from Large Reference Panels.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2018 Aug 31;19:73-96. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-083117-021602. Epub 2018 May 23. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29799802 Review.
-
Genotype Imputation in Genome-Wide Association Studies.Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019 Jun;102(1):e84. doi: 10.1002/cphg.84. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31216114 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison among three variant callers and assessment of the accuracy of imputation from SNP array data to whole-genome sequence level in chicken.BMC Genomics. 2015 Oct 21;16:824. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2059-2. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26486989 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of genetic similarity on imputation accuracy.BMC Genet. 2015 Jul 22;16:90. doi: 10.1186/s12863-015-0248-2. BMC Genet. 2015. PMID: 26193934 Free PMC article.
-
A mega-analysis of expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) provides insight into the regulatory architecture of gene expression variation in liver.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 12;8(1):5865. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24219-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29650998 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of risk loci for postpartum depression in a genome-wide association study.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Nov;78(11):712-720. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13731. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39287932 Free PMC article.
-
Rare Variants Imputation in Admixed Populations: Comparison Across Reference Panels and Bioinformatics Tools.Front Genet. 2019 Apr 3;10:239. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00239. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31001313 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

