Learning the specific quality of taste reinforcement in larval Drosophila
- PMID: 25622533
- PMCID: PMC4302267
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.04711
Learning the specific quality of taste reinforcement in larval Drosophila
Abstract
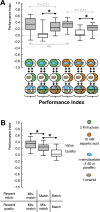
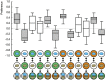
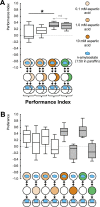
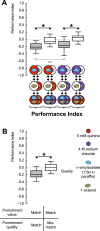
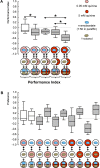
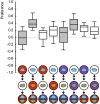
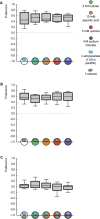
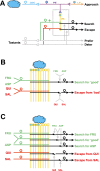
The only property of reinforcement insects are commonly thought to learn about is its value. We show that larval Drosophila not only remember the value of reinforcement (How much?), but also its quality (What?). This is demonstrated both within the appetitive domain by using sugar vs amino acid as different reward qualities, and within the aversive domain by using bitter vs high-concentration salt as different qualities of punishment. From the available literature, such nuanced memories for the quality of reinforcement are unexpected and pose a challenge to present models of how insect memory is organized. Given that animals as simple as larval Drosophila, endowed with but 10,000 neurons, operate with both reinforcement value and quality, we suggest that both are fundamental aspects of mnemonic processing-in any brain.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; memory; neuroscience; olfaction; punishment; reward; taste; valence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An amino-acid mixture can be both rewarding and punishing to larval Drosophilamelanogaster.J Exp Biol. 2019 Nov 28;222(Pt 23):jeb209486. doi: 10.1242/jeb.209486. J Exp Biol. 2019. PMID: 31672727
-
Maggot learning and Synapsin function.J Exp Biol. 2013 Mar 15;216(Pt 6):939-51. doi: 10.1242/jeb.076208. J Exp Biol. 2013. PMID: 23447663 Review.
-
Four individually identified paired dopamine neurons signal taste punishment in larval Drosophila.Elife. 2025 Jun 16;12:RP91387. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91387. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40522297 Free PMC article.
-
Switch-like and persistent memory formation in individual Drosophila larvae.Elife. 2021 Oct 12;10:e70317. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70317. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34636720 Free PMC article.
-
A behavior-based circuit model of how outcome expectations organize learned behavior in larval Drosophila.Learn Mem. 2011 Sep 26;18(10):639-53. doi: 10.1101/lm.2163411. Print 2011 Oct. Learn Mem. 2011. PMID: 21946956 Review.
Cited by
-
Reward signaling in a recurrent circuit of dopaminergic neurons and peptidergic Kenyon cells.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 15;10(1):3097. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11092-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31308381 Free PMC article.
-
Pavlovian Conditioning of Larval Drosophila: An Illustrated, Multilingual, Hands-On Manual for Odor-Taste Associative Learning in Maggots.Front Behav Neurosci. 2017 Apr 19;11:45. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00045. eCollection 2017. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28469564 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol-guided behavior in Drosophila larvae.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 10;11(1):12307. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91677-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34112872 Free PMC article.
-
Modulations of microbehaviour by associative memory strength in Drosophila larvae.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 21;14(10):e0224154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224154. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31634372 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila FIT is a protein-specific satiety hormone essential for feeding control.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 19;8:14161. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14161. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28102207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aso Y, Sitaraman D, Ichinose T, Kaun K, Vogt K, Belliart-Guérin G, Plaçais PY, Robie A, Yamagata N, Schnaitmann C, Rowell WJ, Johnston RM, Ngo TT, Chen N, Korff W, Nitabach MN, Heberlein U, Preat T, Branson KM, Tanimoto H, Rubin GM. Mushroom body output neurons encode valence and guide memory-based action selection in Drosophila. eLife. 2014;4 doi: 10.7554/eLife.04580. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cobb M, Scott K, Pankratz M. Gustation in Drosophila melanogaster. SEB Experimental Biology Series. 2009;63:1–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

