RhoC mediates epidermal growth factor-stimulated migration and invasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25622907
- PMCID: PMC4309735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.12.002
RhoC mediates epidermal growth factor-stimulated migration and invasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
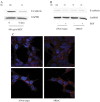
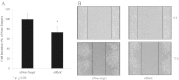
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) where it has been shown to promote tumor cell invasion upon phosphorylation. One mechanism by which EGFR promotes tumor progression is by activating signal cascades that lead to loss of E-cadherin, a transmembrane glycoprotein of the cell-cell adherence junctions; however mediators of these signaling cascades are not fully understood. One such mediator, RhoC, is activated upon a number of external stimuli, such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), but its role as a mediator of EGF-stimulated migration and invasion has not been elucidated in HNSCC. In the present study, we investigate the role of RhoC as a mediator of EGF-stimulated migration and invasion in HNSCC. We show that upon EGF stimulation, EGFR and RhoC were strongly activated in HNSCC. This resulted in activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Akt pathway (PI3K-Akt), phosphorylation of GSK-3β at the Ser(9) residue, and subsequent down regulation of E-cadherin cell surface expression resulting in increased tumor cell invasion. Knockdown of RhoC restored E-cadherin expression and inhibited EGF-stimulated migration and invasion. This is the first report in HNSCC demonstrating the role RhoC plays in mediating EGF-stimulated migration and invasion by down-regulating the PI3K-Akt pathway and E-cadherin expression. RhoC may serve as a treatment target for HNSCC.
Copyright © 2014 Neoplasia Press, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Howlader N., N. A., Krapcho M., Garshell J., Miller D., Altekruse S.F., Kosary C.L., Yu M., Ruhl J., Tatalovich Z. National Cancer Institute; 2014. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2011.
-
- Clark E.A., Golub T.R., Lander E.S., Hynes R.O. Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC. Nature. 2000;406:532–535. - PubMed
-
- van Golen K.L., Wu Z.F., Qiao X.T., Bao L.W., Merajver S.D. RhoC GTPase, a novel transforming oncogene for human mammary epithelial cells that partially recapitulates the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5832–5838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

