Class I histone deacetylase-mediated repression of the proximal promoter of the activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein gene regulates its response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PMID: 25623071
- PMCID: PMC4358108
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.617258
Class I histone deacetylase-mediated repression of the proximal promoter of the activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein gene regulates its response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Abstract
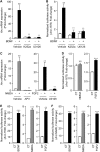
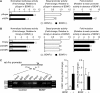
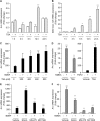
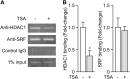
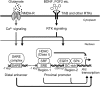
We examined the transcriptional regulation of the activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein gene (Arc), focusing on BDNF-induced Arc expression in cultured rat cortical cells. Although the synaptic activity-responsive element (SARE), located -7 kbp upstream of the Arc transcription start site, responded to NMDA, BDNF, or FGF2, the proximal region of the promoter (Arc/-1679) was activated by BDNF or FGF2, but not by NMDA, suggesting the presence of at least two distinct Arc promoter regions, distal and proximal, that respond to extracellular stimuli. Specificity protein 4 (SP4) and early growth response 1 (EGR1) controlled Arc/-1679 transcriptional activity via the region encompassing -169 to -37 of the Arc promoter. We found that trichostatin A (TSA), a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, significantly enhanced the inductive effects of BDNF or FGF2, but not those of NMDA on Arc expression. Inhibitors of class I/IIb HDACs, SAHA, and class I HDACs, MS-275, but not of class II HDACs, MC1568, enhanced BDNF-induced Arc expression. The enhancing effect of TSA was mediated by the region from -1027 to -1000 bp, to which serum response factor (SRF) and HDAC1 bound. The binding of HDAC1 to this region was reduced by TSA. Thus, Arc expression was suppressed by class I HDAC-mediated mechanisms via chromatin modification of the proximal promoter whereas the inhibition of HDAC allowed Arc expression to be markedly enhanced in response to BDNF or FGF2. These results contribute to our understanding of the physiological role of Arc expression in neuronal functions such as memory consolidation.
Keywords: activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein; brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1); neuron; receptor tyrosine kinase; transcription regulation.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential regulation of Bdnf expression in cortical neurons by class-selective histone deacetylase inhibitors.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.015. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23916482
-
Involvement of SRF coactivator MKL2 in BDNF-mediated activation of the synaptic activity-responsive element in the Arc gene.J Neurochem. 2019 Jan;148(2):204-218. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14596. Epub 2018 Nov 12. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 30244496
-
Postnatal Ethanol Exposure Activates HDAC-Mediated Histone Deacetylation, Impairs Synaptic Plasticity Gene Expression and Behavior in Mice.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 May 27;23(5):324-338. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa017. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32170298 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping synaptic plasticity: the role of activity-mediated epigenetic regulation on gene transcription.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013 Oct;31(6):359-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 May 9. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23665156 Review.
-
Dual mechanisms of regulation of transcription of luteinizing hormone receptor gene by nuclear orphan receptors and histone deacetylase complexes.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;85(2-5):401-14. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(03)00230-9. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12943729 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of hairless mouse strain to bioluminescence imaging of Arc expression in mouse brain.BMC Neurosci. 2017 Jan 23;18(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12868-017-0335-6. BMC Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28114886 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-Dependent Bidirectional Regulation of GAD Expression in a Homeostatic Fashion Is Mediated by BDNF-Dependent and Independent Pathways.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 4;10(8):e0134296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134296. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26241953 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of BDNF Expression and Memory by HDAC Inhibition Requires BET Bromodomain Reader Proteins.J Neurosci. 2019 Jan 23;39(4):612-626. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1604-18.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 30. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30504275 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Transcriptional Activation of the Immediate Early Gene ARC During a Neural Correlate of Classical Conditioning.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov;69(3):380-390. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01367-z. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31273643
-
The lncRNA BDNF-AS is an epigenetic regulator in the human amygdala in early onset alcohol use disorders.Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Feb 6;9(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0367-z. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30728347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lyford G. L., Yamagata K., Kaufmann W. E., Barnes C. A., Sanders L. K., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Lanahan A. A., Worley P. F. (1995) Arc, a growth factor and activity-regulated gene, encodes a novel cytoskeleton-associated protein that is enriched in neuronal dendrites. Neuron 14, 433–445 - PubMed
-
- Kawashima T., Okuno H., Nonaka M., Adachi-Morishima A., Kyo N., Okamura M., Takemoto-Kimura S., Worley P. F., Bito H. (2009) Synaptic activity-responsive element in the Arc/Arg3.1 promoter essential for synapse-to-nucleus signaling in activated neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 316–321 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

