Clinical Experience With Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases
- PMID: 25624436
- PMCID: PMC4451171
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.0539
Clinical Experience With Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases
Abstract
Purpose: Crizotinib is an oral kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The clinical benefits of crizotinib in patients with brain metastases have not been previously studied.
Patients and methods: Patients with advanced ALK-rearranged NSCLC enrolled onto clinical trial PROFILE 1005 or 1007 (randomly assigned to crizotinib) were included in this retrospective analysis. Patients with asymptomatic brain metastases (nontarget or target lesions) were allowed to enroll. Tumor assessments were evaluated every 6 weeks using RECIST (version 1.1).
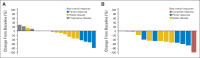
Results: At baseline, 31% of patients (275 of 888) had asymptomatic brain metastases; 109 had received no prior and 166 had received prior brain radiotherapy as treatment. Among patients with previously untreated asymptomatic brain metastases, the systemic disease control rate (DCR) at 12 weeks was 63% (95% CI, 54% to 72%), the intracranial DCR was 56% (95% CI, 46% to 66%), and the median intracranial time to progression (TTP) was 7 months (95% CI, 6.7 to 16.4). Among patients with previously treated brain metastases, the systemic DCR was 65% (95% CI, 57% to 72%), the intracranial DCR was 62% (95% CI, 54% to 70%), and the median intracranial TTP was 13.2 months (95% CI, 9.9 to not reached). Patients with systemic disease control were also likely to experience intracranial disease control at 12 weeks (correlation coefficient, 0.7652; P < .001). Among patients without baseline brain metastases who developed progressive disease (n = 253) after initiation of crizotinib, 20% were diagnosed with brain metastases.
Conclusion: Crizotinib was associated with systemic and intracranial disease control in patients with ALK-rearranged NSCLC who were ALK inhibitor naive and had brain metastases. However, progression of preexisting or development of new intracranial lesions while receiving therapy was a common manifestation of acquired resistance to crizotinib.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00932451 NCT00932893.
© 2015 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Garraway LA, Verweij J, Ballman KV. Precision oncology: An overview. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:1803–1805. - PubMed
-
- Cheng L, Alexander RE, Maclennan GT, et al. Molecular pathology of lung cancer: Key to personalized medicine. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:347–369. - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

