Direct inhibition of oncogenic KRAS by hydrocarbon-stapled SOS1 helices
- PMID: 25624485
- PMCID: PMC4330742
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1413185112
Direct inhibition of oncogenic KRAS by hydrocarbon-stapled SOS1 helices
Abstract
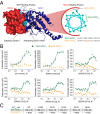
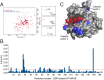
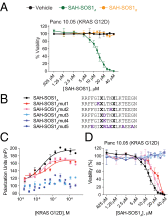
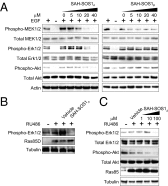
Activating mutations in the Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) underlie the pathogenesis and chemoresistance of ∼ 30% of all human tumors, yet the development of high-affinity inhibitors that target the broad range of KRAS mutants remains a formidable challenge. Here, we report the development and validation of stabilized alpha helices of son of sevenless 1 (SAH-SOS1) as prototype therapeutics that directly inhibit wild-type and mutant forms of KRAS. SAH-SOS1 peptides bound in a sequence-specific manner to KRAS and its mutants, and dose-responsively blocked nucleotide association. Importantly, this functional binding activity correlated with SAH-SOS1 cytotoxicity in cancer cells expressing wild-type or mutant forms of KRAS. The mechanism of action of SAH-SOS1 peptides was demonstrated by sequence-specific down-regulation of the ERK-MAP kinase phosphosignaling cascade in KRAS-driven cancer cells and in a Drosophila melanogaster model of Ras85D(V12) activation. These studies provide evidence for the potential utility of SAH-SOS1 peptides in neutralizing oncogenic KRAS in human cancer.
Keywords: RAS; SOS1; cancer; inhibitor; stapled peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: L.D.W. is a scientific advisory board member and consultant for Aileron Therapeutics.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

