Experimental infection of Z:ZCLA Mongolian gerbils with human hepatitis E virus
- PMID: 25624719
- PMCID: PMC4299338
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.862
Experimental infection of Z:ZCLA Mongolian gerbils with human hepatitis E virus
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether Z:ZCLA Mongolian gerbils are readily susceptible to infection by human hepatitis E virus (HEV).
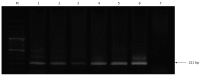
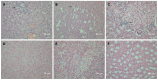
Methods: Z:ZCLA Mongolian gerbils were infected with a clinical HEV strain isolated from an acute hepatitis E patient, and virus pathogenesis was assessed in this host. Non-infected gerbils served as the control group. Feces samples from gerbils were collected weekly for reverse transcription-nested polymerase chain reaction. Serum anti-HEV IgG and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. At sacrifice, each animal's liver, spleen and kidney were collected for histopathologic examination.
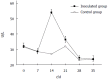
Results: HEV-infected gerbils showed fatigue, with histopathological changes observed in the liver, spleen and kidney. HEV RNA was detected in fecal samples taken at day 7 after inoculation and the detectable levels lasted out to day 42 after inoculation. Interestingly, ALT levels were only moderately increased in the HEV-infected animals compared with the non-infected control group.
Conclusion: Z:ZCLA Mongolian gerbils are susceptible to human HEV.
Keywords: Hepatitis E virus; Infection; Interspecies transmission; Mongolian gerbils; Zoonosis.
Figures
References
-
- Purcell RH, Emerson SU. Hepatitis E virus. In: Knipe , DM , Howley PM, eds , editors. Fields virology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. pp. 3051–3061.
-
- Teshale EH, Hu DJ, Holmberg SD. The two faces of hepatitis E virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:328–334. - PubMed
-
- Huang FF, Haqshenas G, Guenette DK, Halbur PG, Schommer SK, Pierson FW, Toth TE, Meng XJ. Detection by reverse transcription-PCR and genetic characterization of field isolates of swine hepatitis E virus from pigs in different geographic regions of the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:1326–1332. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

