Hes1, an important gene for activation of hepatic stellate cells, is regulated by Notch1 and TGF-β/BMP signaling
- PMID: 25624721
- PMCID: PMC4299340
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.878
Hes1, an important gene for activation of hepatic stellate cells, is regulated by Notch1 and TGF-β/BMP signaling
Abstract
Aim: To determine the role of Notch1 and Hes1 in regulating the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and whether Hes1 is regulated by transforming growth factor (TGF)/bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling.
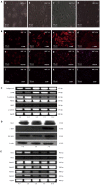
Methods: Immunofluorescence staining was used to detect the expression of desmin, glial fibrillary acidic protein and the myofibroblastic marker α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) after freshly isolated, normal rat HSCs had been activated in culture for different numbers of days (0, 1, 3, 7 and 10 d). The expression of α-SMA, collagen1α2 (COL1α2), Notch receptors (Notch1-4), and the Notch target genes Hes1 and Hey1 were analyzed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Luciferase reporter assays and Western blot were used to study the regulation of α-SMA, COL1α1, COL1α2 and Hes1 by NICD1, Hes1, CA-ALK3, and CA-ALK5 in HSC-T6 cells. Moreover, the effects of inhibiting Hes1 function in HSC-T6 cells using a Hes1 decoy were also investigated.
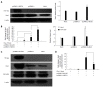
Results: The expression of Notch1 and Hes1 mRNAs was significantly down-regulated during the culture of freshly isolated HSCs. In HSC-T6 cells, Notch1 inhibited the promoter activities of α-SMA, COL1α1 and COL1α2. On the other hand, Hes1 enhanced the promoter activities of α-SMA and COL1α2, and this effect could be blocked by inhibiting Hes1 function with a Hes1 decoy. Furthermore, co-transfection of pcDNA3-CA-ALK3 (BMP signaling activin receptor-like kinase 3) and pcDNA3.1-NICD1 further increased the expression of Hes1 compared with transfection of either vector alone in HSC-T6 cells, while pcDNA3-CA-ALK5 (TGF-β signaling activin receptor-like kinase 5) reduced the effect of NICD1 on Hes1 expression.
Conclusion: Selective interruption of Hes1 or maintenance of Hes1 at a reasonable level decreases the promoter activities of α-SMA and COL1α2, and these conditions may provide an anti-fibrotic strategy against hepatic fibrosis.
Keywords: Hepatic fibrosis; Hepatic stellate cells; Hes1; Notch1; TGF-β/BMP.
Figures


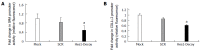
Similar articles
-
Gremlin1 Accelerates Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation Through Upregulation of TGF-Beta Expression.DNA Cell Biol. 2017 Jul;36(7):603-610. doi: 10.1089/dna.2017.3707. Epub 2017 May 3. DNA Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28467108
-
Saikosaponin A of Bupleurum chinense (Chaihu) elevates bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP-4) during hepatic stellate cell activation.Phytomedicine. 2013 Nov 15;20(14):1330-5. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Phytomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23969230
-
Iron Enhances Hepatic Fibrogenesis and Activates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling in Murine Hepatic Stellate Cells.Am J Med Sci. 2018 Feb;355(2):183-190. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Am J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29406047
-
TGF-β in Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrogenesis-Updated 2019.Cells. 2019 Nov 11;8(11):1419. doi: 10.3390/cells8111419. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31718044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of thymosin Beta 4 in liver fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 May 8;16(5):10624-35. doi: 10.3390/ijms160510624. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26006229 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differentially expressed lncRNAs in liver tissues of TX mice with hepatolenticular degeneration.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 14;11(1):1377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80635-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33446761 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibitory effects of the novel Lactobacillus cocktail on colorectal cancer development through modulating BMP signaling pathway: In vitro and in vivo study.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 19;10(17):e36554. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36554. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281652 Free PMC article.
-
Notch in fibrosis and as a target of anti-fibrotic therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Jun;108:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27107790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The IGF2BP3/Notch/Jag1 pathway: A key regulator of hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis in liver fibrosis.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Aug;14(8):e1793. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1793. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39113232 Free PMC article.
-
Consequences of Amyloid-β Deficiency for the Liver.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 May;11(18):e2307734. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307734. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38430535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wells RG. The role of matrix stiffness in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:S158–S161. - PubMed
-
- Bataller R, Brenner DA. Hepatic stellate cells as a target for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21:437–451. - PubMed
-
- Purps O, Lahme B, Gressner AM, Meindl-Beinker NM, Dooley S. Loss of TGF-beta dependent growth control during HSC transdifferentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;353:841–847. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

