PET imaging of apoptosis in tumor-bearing mice and rabbits after paclitaxel treatment with (18)F(-)Labeled recombinant human His10-annexin V
- PMID: 25625024
- PMCID: PMC4299778
PET imaging of apoptosis in tumor-bearing mice and rabbits after paclitaxel treatment with (18)F(-)Labeled recombinant human His10-annexin V
Abstract
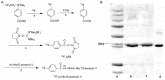
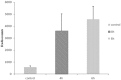
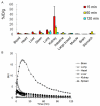
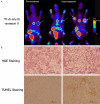
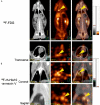
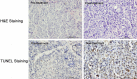
Monitoring response to chemo- or radiotherapy is of great importance in clinical practice. Apoptosis imaging serves as a very useful tool for the early evaluation of tumor response. The goal of this study was PET imaging of apoptosis with (18)F-labeled recombinant human annexin V linked with 10 histidine tag ((18)F-rh-His10-annexin V) in nude mice bearing an A549 tumor and rabbits bearing a VX2 lung cancer after paclitaxel therapy. (18)F-rh-His10-annexin V was prepared by conjugation of rh-His10-annexin V with N-succinimidyl 4-[(18)F]fluorobenzoate. Biodistribution was determined in mice by the dissection method and small-animal PET. Single-dose paclitaxel (175 mg/m(2)) was used to induce apoptosis in A549 and VX2 tumor models. (18)F-rh-His10-annexin V was injected into A549 mice and VX rabbits to acquire dynamic and static PET images 72 h after paclitaxel treatment. The uptake of (18)F-rh-His10-annexin V in apoptotic cells 4 h after induction was 6.45±0.52 fold higher than that in non-induced cells. High focal uptake of (18)F-rh-His10-annexin V was visualized in A549 (SUVmax: 0.35±0.13) and VX2 (0.41±0.23) tumor models after paclitaxel treatment, whereas lower uptake was found in the corresponding tumors before treatment (A549 SUVmax: 0.04±0.02; VX2: 0.009±0.002). The apoptotic index was 75.61±11.56% in the treated VX2 cancer, much higher than that in the untreated VX2 (8.03±2.81%). This study demonstrated the feasibility of (18)F-rh-His10-annexin V for the detection of apoptosis after chemotherapy in A549 and VX2 tumor models.
Keywords: Apoptosis; molecular imaging; recombinant human His10-annexin V; tumor response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A preliminary study of imaging paclitaxel-induced tumor apoptosis with (99)Tc(m)-His10-Annexin V.Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(15):2928-33. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013. PMID: 23924470
-
Evaluation of chemotherapy response in VX2 rabbit lung cancer with 18F-labeled C2A domain of synaptotagmin I.J Nucl Med. 2011 Apr;52(4):592-9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.081588. Epub 2011 Mar 18. J Nucl Med. 2011. PMID: 21421722 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of adenosine preconditioning with 99mTc-His10-annexin V in a porcine model of myocardium ischemia and reperfusion injury: preliminary study.Nucl Med Biol. 2011 May;38(4):567-74. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2010.11.002. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Nucl Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21531294
-
Monitoring apoptosis in real time.Cancer J. 2002 Mar-Apr;8(2):82-92. doi: 10.1097/00130404-200203000-00002. Cancer J. 2002. PMID: 11999952 Review.
-
The imaging of apoptosis with the radiolabeled annexin V: optimal timing for clinical feasibility.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2004 Feb;3(1):23-32. doi: 10.1177/153303460400300103. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2004. PMID: 14750890 Review.
Cited by
-
[18F]ML-10 PET: Initial Experience in Glioblastoma Multiforme Therapy Response Assessment.Tomography. 2016 Dec;2(4):317-324. doi: 10.18383/j.tom.2016.00175. Tomography. 2016. PMID: 30042965 Free PMC article.
-
Avenues to molecular imaging of dying cells: Focus on cancer.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(6):1713-1768. doi: 10.1002/med.21495. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29528513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preliminary Study of a 1,5-Benzodiazepine-Derivative Labelled with Indium-111 for CCK-2 Receptor Targeting.Molecules. 2021 Feb 9;26(4):918. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040918. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33572353 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin A: Cell Death, Inflammation, and Translational Medicine.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Apr 26;18:5655-5672. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S511439. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40309306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumor Model: A Review of Clinical, Biology, Histology, and Tumor Microenvironment Characteristics.Front Oncol. 2022 May 10;12:871829. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.871829. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35619923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Michaelis LC, Ratain MJ. Measuring response in a post-RECIST world: from black and white to shades of grey. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:409–14. - PubMed
-
- Goffin J, Baral S, Tu D, Nomikos D, Seymour L. Objective responses in patients with malignant melanoma or renal cell cancer in early clinical studies do not predict regulatory approval. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5928–34. - PubMed
-
- Weber WA. Positron emission tomography as an imaging biomarker. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:3282–92. - PubMed
-
- Gambhir SS. Molecular imaging of cancer with positron emission tomography. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:683–93. - PubMed
-
- Juweid ME, Cheson BD. Positron-emission tomography and assessment of cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:496–507. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
