In vivo evaluation of the accuracy of working length determination using an electronic apex locater IPEX (NSK) on vital uninfected teeth and teeth with radiographic evidence of periapical lesions
- PMID: 25625080
- PMCID: PMC4304060
- DOI: 10.4103/2231-0762.149042
In vivo evaluation of the accuracy of working length determination using an electronic apex locater IPEX (NSK) on vital uninfected teeth and teeth with radiographic evidence of periapical lesions
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the accuracy of working length determination of an electronic apex locator, IPEX, on vital uninfected teeth and teeth with radiographic evidence of periapical lesions.
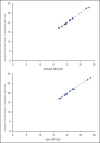
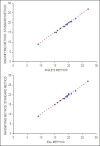
Materials and methods: Twenty vital and uninfected teeth and 16 teeth with a single canal and matured apices and having radiographic evidence of periapical lesions of 5-10 mm were taken for this study. Access cavities were prepared and pulp was considered to be vital if bleeding was present upon entering the chambers. No. 15 k-type file was used to determine the working length. X-rays were taken to determine the working length using Ingle's method, followed by determination using the electronic apex locator, IPEX. Teeth were then observed under 45 × magnification using stereomicroscope. No 15 k-type file was maneuvered till the emergence of the tip was seen and the real length of the tooth was thus measured in the instrument up to 0.5 mm accuracy using stereomicroscope.
Results: The data were duly collected and entered, and the statistical analysis was done using Student's t test. In uninfected teeth, IPEX was found to be more reliable than Ingle's radiographic technique, but this was not statistically significant. In case of teeth with radiographic evidence of periapical lesions, the radiographic method appeared to be relatively more dependable; however, this difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: For rendering effective root canal procedure, both radiographs and electronic apex locators have important roles to play.
Keywords: Electronic apex locator; IPEX; Ingle's method; periapical lesions; radiographs; working length.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Comparative Evaluation of Accuracy of New-generation Electronic Apex Locator with Conventional Radiography to determine Working Length in Primary Teeth: An in vivo Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2017 Jan-Mar;10(1):34-36. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1403. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2017. PMID: 28377652 Free PMC article.
-
An In Vitro Comparison of Propex II Apex Locator to Standard Radiographic Method.Iran Endod J. 2013 Summer;8(3):114-7. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Iran Endod J. 2013. PMID: 23922572 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo Study to Evaluate the Effect of Instrument Size on the Accuracy of Three Different Apex Locators when Various Irrigation Solutions are used in Vital and Non-Vital Teeth.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2023 Jul;15(Suppl 2):S1156-S1159. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_182_23. Epub 2023 Apr 28. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2023. PMID: 37693955 Free PMC article.
-
An in vivo radiographic evaluation of the accuracy of Apex and iPex electronic Apex locators.Braz Dent J. 2012;23(1):54-8. doi: 10.1590/s0103-64402012000100010. Braz Dent J. 2012. PMID: 22460316
-
Determination of working length for teeth with wide or immature apices: a review.Int Endod J. 2013 Jun;46(6):483-91. doi: 10.1111/iej.12032. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Int Endod J. 2013. PMID: 23216284 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors influencing the accuracy of electronic apex locators: A scoping review.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2025 Jun 27;22:26. doi: 10.4103/drj.drj_634_23. eCollection 2025. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2025. PMID: 40655901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Working Length Determination Accuracy by Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Primary Teeth.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022;15(Suppl 1):S92-S96. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2330. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35645504 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of File Size and Type and Irrigation Solutions on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study on Canine Teeth.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8594087. doi: 10.1155/2016/8594087. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27747242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martínez-Lozano MA, Forner-Navarro L, Sánchez-Cortés JL, Llena-Puy C. Methodological considerations in the determination of the working length. Int Endod J. 2001;34:371–6. - PubMed
-
- Kim E, Lee SJ. Electronic apex locator. Dent Clin North Am. 2004;48:35–54. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K. Experimental study on iontophoresis. J Jap Stomatol. 1942;16:411–29.
-
- Sunada I. New methods for measuring length of root canals. J Dent Res. 1962;41:375–87.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

