The effect of pulp and seed extract of Citrullus Colocynthis, as an antidaibetic medicinal herb, on hepatocytes glycogen stores in diabetic rabbits
- PMID: 25625097
- PMCID: PMC4298881
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.148230
The effect of pulp and seed extract of Citrullus Colocynthis, as an antidaibetic medicinal herb, on hepatocytes glycogen stores in diabetic rabbits
Abstract
Background: Medicinal herbs such as Citrullus Colocynthis (C.C) have been used traditionally in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. However therapeutic applications and adverse effects of C.C and its natural variants are not determined well. The current work investigates the effects of pulp and seed extract of C.C on hepatocyte's glycogen stores.
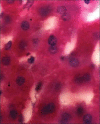
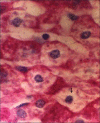
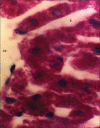
Materials and methods: Thirty six male rabbits were divided into six groups (control and diabetic) randomly. Alloxan was used in order to induce diabetes mellitus in animals. Among 5 diabetic groups, one remained as control and the rest received 100 and 200 mg/kg/day of either pulp or seed extract. One month later, animals were sacrificed and their liver specimen fixed in 10% Formalin was stained with periodic acid schiff (PAS) for light microscopic scanning.
Results: PAS staining of hepatocytes revealed large amounts of glycogen stores in diabetic animals treated with pulp and seed extracts of C.C, contrary with non-treated diabetic rabbits. Sites of glycogen deposition were also different in animals treated with seed extract (P < 0.0001). No hepatic congestion was seen in treated animals. Dose escalation has no effect on the obtained results.
Conclusions: The anti-diabetic effects of C.C can be explained by its effects on accumulation of glycogen stores in hepatocytes. The importance of varied sites of glycogen deposition by the application of C.C needs to be determined.
Keywords: Citrullus Colocynthis; diabetes mellitus; glycogen stores.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Vijan S, Hayward RA. Treatment of hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Blood pressure goals, choice of agents, and setting priorities in diabetes care. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:593–602. - PubMed
-
- Jung M, Park M, Lee HC, Kang YH, Kang ES, Kim SK. Antidiabetic agents from medicinal plants. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13:1203–18. - PubMed
-
- Feng CG, Zhang LX, Liu X. Progress in research of aldose reductase inhibitors in traditional medicinal herbs. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2005;30:1496–500. - PubMed
-
- Vuksan V, Sievenpiper JL. Sievenpiper, Herbal remedies in the management of diabetes: Lessons learned from the study of ginseng. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2005;15:149–60. - PubMed
-
- Huseini HF, Darvishzadeh F, Heshmat R, Jafariazar Z, Raza M, Larijani B. The clinical investigation of Citrullus colocynthis (L.) schrad fruit in treatment of type II diabetic patients: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res. 2009;23:1186–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

