The effects of two polymorphisms on p21cip1 function and their association with Alzheimer's disease in a population of European descent
- PMID: 25625488
- PMCID: PMC4308198
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114050
The effects of two polymorphisms on p21cip1 function and their association with Alzheimer's disease in a population of European descent
Abstract
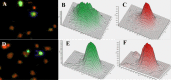
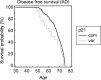
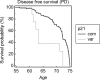
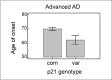
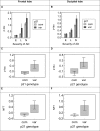
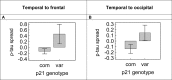
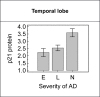
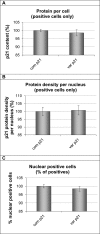
With the exception of ApoE4, genome-wide association studies have failed to identify strong genetic risk factors for late-onset Alzheimer's disease, despite strong evidence of heritability, suggesting that many low penetrance genes may be involved. Additionally, the nature of the identified genetic risk factors and their relation to disease pathology is also largely obscure. Previous studies have found that a cancer-associated variant of the cell cycle inhibitor gene p21cip1 is associated with increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. The aim of this study was to confirm this association and to elucidate the effects of the variant on protein function and Alzheimer-type pathology. We examined the association of the p21cip1 variant with Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease with dementia. The genotyping studies were performed on 719 participants of the Oxford Project to Investigate Memory and Ageing, 225 participants of a Parkinson's disease DNA bank, and 477 participants of the Human Random Control collection available from the European Collection of Cell Cultures. The post mortem studies were carried out on 190 participants. In the in-vitro study, human embryonic kidney cells were transfected with either the common or rare p21cip1 variant; and cytometry was used to assess cell cycle kinetics, p21cip1 protein expression and sub-cellular localisation. The variant was associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease with dementia, relative to age matched controls. Furthermore, the variant was associated with an earlier age of onset of Alzheimer's disease, and a more severe phenotype, with a primary influence on the accumulation of tangle pathology. In the in-vitro study, we found that the SNPs reduced the cell cycle inhibitory and anti-apoptotic activity of p21cip1. The results suggest that the cancer-associated variant of p21cip1 may contribute to the loss of cell cycle control in neurons that may lead to Alzheimer-type neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mutations in ABCA7 in a Belgian cohort of Alzheimer's disease patients: a targeted resequencing study.Lancet Neurol. 2015 Aug;14(8):814-822. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00133-7. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Lancet Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26141617
-
Genetic variation within endolysosomal system is associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2018 Sep 1;141(9):2711-2720. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy197. Brain. 2018. PMID: 30124770
-
SNPs associated with cerebrospinal fluid phospho-tau levels influence rate of decline in Alzheimer's disease.PLoS Genet. 2010 Sep 16;6(9):e1001101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001101. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20862329 Free PMC article.
-
Role of tau versus TDP-43 pathology on medial temporal lobe atrophy in aging and Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Feb;21(2):e14582. doi: 10.1002/alz.14582. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 39985478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Senescence: A DNA damage response and its role in aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Aging. 2024 Mar 21;4:1292053. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2023.1292053. eCollection 2023. Front Aging. 2024. PMID: 38596783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GSK3-ARC/Arg3.1 and GSK3-Wnt signaling axes trigger amyloid-β accumulation and neuroinflammation in middle-aged Shugoshin 1 mice.Aging Cell. 2020 Oct;19(10):e13221. doi: 10.1111/acel.13221. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 32857910 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Senescence in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Feb 11;14:16. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00016. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32116562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogenic differentiation factor 1 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by suppressing the p53/p21 axis.Cancer Sci. 2020 Jan;111(1):175-185. doi: 10.1111/cas.14233. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31715070 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage and neurodegenerative phenotypes in aged Ciz1 null mice.Neurobiol Aging. 2018 Feb;62:180-190. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.10.014. Neurobiol Aging. 2018. PMID: 29154038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A, Brayne C, Aarsland D, et al. (2011) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 377: 1019–1031. - PubMed
-
- Gatz M, Reynolds CA, Fratiglioni L, Johansson B, Mortimer JA, et al. (2006) Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63: 168–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

