Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for point-of-care detection of asymptomatic low-density malaria parasite carriers in Zanzibar
- PMID: 25627037
- PMCID: PMC4318361
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-015-0573-y
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for point-of-care detection of asymptomatic low-density malaria parasite carriers in Zanzibar
Abstract
Background: Asymptomatic, low parasite density malaria infections are difficult to detect with currently available point-of-care diagnostics. This study piloted a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) kit for field-friendly, high-throughput detection of asymptomatic malaria infections during mass screening and treatment (MSAT) in Zanzibar, a malaria pre-elimination setting.
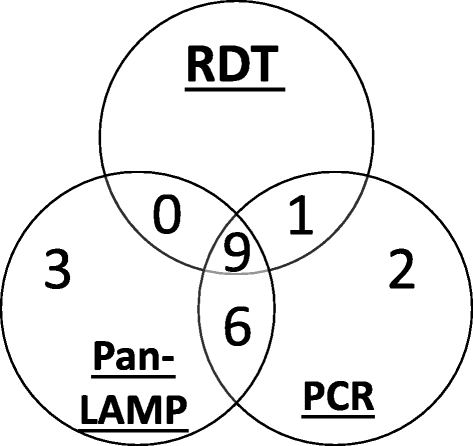
Methods: Screening took place in three known hotspot areas prior to the short rains in November. Finger-prick blood was taken for screening by rapid diagnostic test (RDT) and LAMP and collected on filter paper for subsequent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analyses. LAMP results were compared to RDT and to PCR using McNemar's test.
Results: Approximately 1,000 people were screened. RDT detected ten infections (1.0% (95% CI 0.3-1.6)) whilst both LAMP and PCR detected 18 (1.8% (95% CI 0.9-2.6)) infections. However, PCR identified three infections that LAMP did not detect and vice versa. LAMP testing was easy to scale-up in field conditions requiring minimal training and equipment, with results ready one to three hours after screening.
Conclusions: Despite lower than expected prevalence, LAMP detected a higher number of infections than the currently used diagnostic, RDT. LAMP is a field-friendly, sensitive diagnostic test that could be useful for MSAT malaria campaigns which require quick results to enable prompt treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Programme ZME. Malaria Epidemic Early Detection System. 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical