Temporal sequence of activation of cells involved in purinergic neurotransmission in the colon
- PMID: 25627983
- PMCID: PMC4405753
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.287599
Temporal sequence of activation of cells involved in purinergic neurotransmission in the colon
Abstract
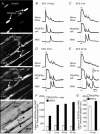
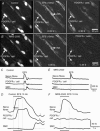
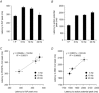
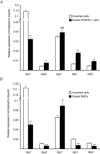
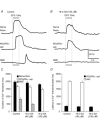
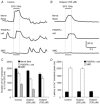
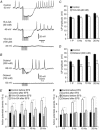
Key points: Platelet derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRα(+) ) cells in colonic muscles are innervated by enteric inhibitory motor neurons. PDGFRα(+) cells generate Ca(2+) transients in response to exogenous purines and these responses were blocked by MRS-2500. Stimulation of enteric neurons, with cholinergic and nitrergic components blocked, evoked Ca(2+) transients in PDGFRα(+) and smooth muscle cells (SMCs). Responses to nerve stimulation were abolished by MRS-2500 and not observed in muscles with genetic deactivation of P2Y1 receptors. Ca(2+) transients evoked by nerve stimulation in PDGFRα(+) cells showed the same temporal characteristics as electrophysiological responses. PDGFRα(+) cells express gap junction genes, and drugs that inhibit gap junctions blocked neural responses in SMCs, but not in nerve processes or PDGFRα(+) cells. PDGFRα(+) cells are directly innervated by inhibitory motor neurons and purinergic responses are conducted to SMCs via gap junctions.
Abstract: Interstitial cells, known as platelet derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRα(+) ) cells, are closely associated with varicosities of enteric motor neurons and suggested to mediate purinergic hyperpolarization responses in smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract (GI), but this concept has not been demonstrated directly in intact muscles. We used confocal microscopy to monitor Ca(2+) transients in neurons and post-junctional cells of the murine colon evoked by exogenous purines or electrical field stimulation (EFS) of enteric neurons. EFS (1-20 Hz) caused Ca(2+) transients in enteric motor nerve processes and then in PDGFRα(+) cells shortly after the onset of stimulation (latency from EFS was 280 ms at 10 Hz). Responses in smooth muscle cells (SMCs) were typically a small decrease in Ca(2+) fluorescence just after the initiation of Ca(2+) transients in PDGFRα(+) cells. Upon cessation of EFS, several fast Ca(2+) transients were noted in SMCs (rebound excitation). Strong correlation was noted in the temporal characteristics of Ca(2+) transients evoked in PDGFRα(+) cells by EFS and inhibitory junction potentials (IJPs) recorded with intracellular microelectrodes. Ca(2+) transients and IJPs elicited by EFS were blocked by MRS-2500, a P2Y1 antagonist, and absent in P2ry1((-/-)) mice. PDGFRα(+) cells expressed gap junction genes, and gap junction uncouplers, 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (18β-GA) and octanol blocked Ca(2+) transients in SMCs but not in neurons or PDGFRα(+) cells. IJPs recorded from SMCs were also blocked. These findings demonstrate direct innervation of PDGFRα(+) cells by motor neurons. PDGFRα(+) cells are primary targets for purinergic neurotransmitter(s) in enteric inhibitory neurotransmission. Hyperpolarization responses are conducted to SMCs via gap junctions.
© 2015 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2015 The Physiological Society.
Figures



Comment in
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α-positive cells: new players in nerve-mediated purinergic responses in the colon.J Physiol. 2015 Apr 15;593(8):1765-6. doi: 10.1113/JP270259. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25871557 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Banks BE, Brown C, Burgess GM, Burnstock G, Claret M, Cocks TM. Jenkinson DH. Apamin blocks certain neurotransmitter-induced increases in potassium permeability. Nature. 1979;282:415–417. - PubMed
-
- Baranska J, Czajkowski R. Sabala P. Cross-talks between nucleotide receptor-induced signaling pathways in serum-deprived and non-starved glioma C6 cells. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2004;44:219–232. - PubMed
-
- Bitar KN, Said SI, Weir GC, Saffouri B. Makhlouf GM. Neural release of vasoactive intestinal peptide from the gut. Gastroenterology. 1980;79:1288–1294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

