Positive regulation of Rho GTPase activity by RhoGDIs as a result of their direct interaction with GAPs
- PMID: 25628036
- PMCID: PMC4312443
- DOI: 10.1186/s12918-015-0143-5
Positive regulation of Rho GTPase activity by RhoGDIs as a result of their direct interaction with GAPs
Abstract
Background: Rho GTPases function as molecular switches in many different signaling pathways and control a wide range of cellular processes. Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitors (RhoGDIs) regulate Rho GTPase signaling and can function as both negative and positive regulators. The role of RhoGDIs as negative regulators of Rho GTPase signaling has been extensively investigated; however, little is known about how RhoGDIs act as positive regulators. Furthermore, it is unclear how this opposing role of GDIs influences the Rho GTPase cycle. We constructed ordinary differential equation models of the Rho GTPase cycle in which RhoGDIs inhibit the regulatory activities of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) by interacting with them directly as well as by sequestering the Rho GTPases. Using this model, we analyzed the role of RhoGDIs in Rho GTPase signaling.
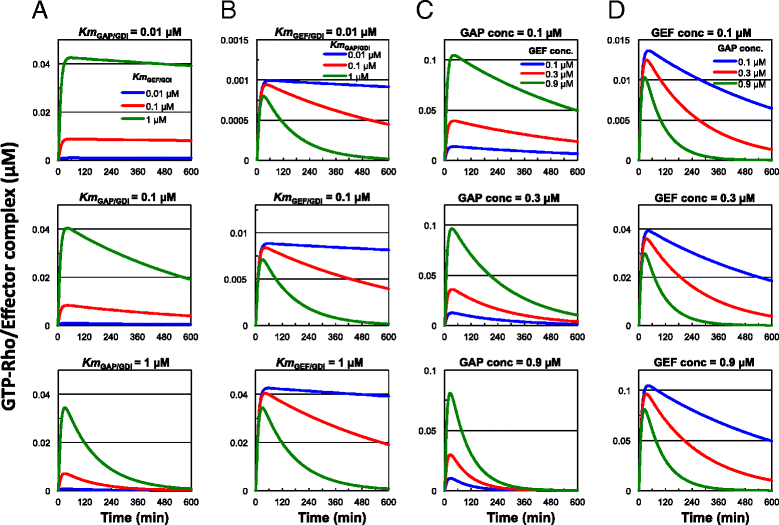
Results: The model constructed in this study showed that the functions of GEFs and GAPs are integrated into Rho GTPase signaling through the interactions of these regulators with GDIs, and that the negative role of GDIs is to suppress the overall Rho activity by inhibiting GEFs. Furthermore, the positive role of GDIs is to sustain Rho activation by inhibiting GAPs under certain conditions. The interconversion between transient and sustained Rho activation occurs mainly through changes in the affinities of GDIs to GAPs and the concentrations of GAPs.
Conclusions: RhoGDIs positively regulate Rho GTPase signaling primarily by interacting with GAPs and may participate in the switching between transient and sustained signals of the Rho GTPases. These findings enhance our understanding of the physiological roles of RhoGDIs and Rho GTPase signaling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Underappreciated roles for Rho GDP dissociation inhibitors (RhoGDIs) in cell function: Lessons learned from the pancreatic islet β-cell.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;197:114886. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114886. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34968495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs.Physiol Rev. 2013 Jan;93(1):269-309. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00003.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23303910 Review.
-
Regulation of Rho GTPases by RhoGDIs in Human Cancers.Cells. 2019 Sep 5;8(9):1037. doi: 10.3390/cells8091037. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31492019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GDIs: central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation.Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;15(7):356-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.05.001. Trends Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15921909 Review.
-
Rho GTPase regulatory proteins in podocytes.Kidney Int. 2021 Feb;99(2):336-345. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.08.035. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Kidney Int. 2021. PMID: 33122025 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics Analysis of Proteotoxic Stress Response in In-Vitro Human Neuronal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 20;25(12):6787. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126787. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928492 Free PMC article.
-
Underappreciated roles for Rho GDP dissociation inhibitors (RhoGDIs) in cell function: Lessons learned from the pancreatic islet β-cell.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;197:114886. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114886. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34968495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian Disruption Primes Myofibroblasts for Accelerated Activation as a Mechanism Underpinning Fibrotic Progression in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Cells. 2023 Jun 8;12(12):1582. doi: 10.3390/cells12121582. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371052 Free PMC article.
-
RhoGDI2 up-regulates P-glycoprotein expression via Rac1 in gastric cancer cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2015 Apr 15;15:41. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0190-4. eCollection 2015. Cancer Cell Int. 2015. PMID: 25901126 Free PMC article.
-
Friend leukemia virus integration 1 activates the Rho GTPase pathway and is associated with metastasis in breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 15;6(27):23764-75. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4350. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26156017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nancy V, Callebaut I, El Marjou A, de Gunzburg J. The delta subunit of retinal rod cGMP phosphodiesterase regulates the membrane association of Ras and Rap GTPases. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(17):15076–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

